Events on July 17, 2015

SCI, CIBC and MRL Presents:
Summer Course on Image-Based Biomedical Modeling
July 13 - July 23, 2015 day 5 of 11
10:00am
Park City, Utah
Description:
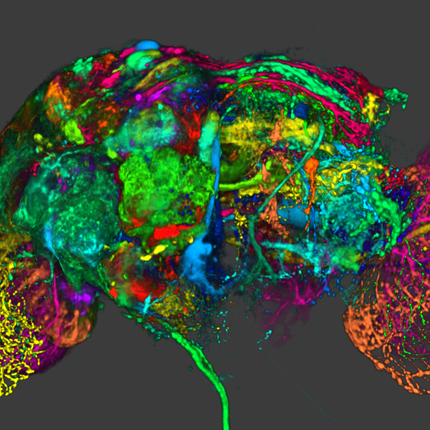
This course offers field-specific expertise and hands-on experience solving bioelectric or biomechanical problems that arise in current biomedical research and clinical practice. Participants will receive training in numerical methods, image analysis, and computational tools necessary to carry out end-to-end, image based, subject specific simulations in bioelectricity or biomechanics, using freely available software.
Presented by the Scientific Computing and Imaging (SCI) Institute, the Center for Integrative Biomedical Computing (CIBC), and the Musculoskeletal Research Laboratories (MRL).

Sumedha Singla Presents:
M.S Project Defense: SSM and FEA Integrated Approach to FAI and Dysplasia
July 17, 2015 at 9:30am for 1hr
Evans Conference Room, WEB 3780
Warnock Engineering Building, 3rd floor.
Abstract:
Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) and acetabular dysplasia are two pathoanatomical conditions of the hip. In our current research, experts in medicine, biomechanics and computer science collaborate to improve the anatomical and functional understanding of FAI and dysplasia using statistical shape modeling (SSM) and finite element analysis (FEA). SSM can quantify complex anatomy and variation within and between populations of interest based on 3D image data and delineate which clinical parameters are predictive of shape. The finite element (FE) method can be used to predict patient-specific tissue mechanics from 3D image data.
Our project, aims at integrating, ShapeWorks (an open-source distribution for constructing compact statistical point-based models of ensembles of similar shapes) with FEBio (an open sources, nonlinear finite element solver, specifically designed for biomechanical applications) to enable flexible and robust analyses of shape and function. Thereafter, we will use the integrated software to quantify the variation in femoral head anatomy and acetabular rim coverage among normal hips and hips with cam/pincer/mixed type FAI. The other purpose of this study was to quantify and compare variation in proximal femoral head cortical bone thickness and total volume of the cortex in normal controls and patients with cam-type FAI using statistical shape modeling. Further we are simulating the bone resection scenarios to understand the implication of surgery in the femoral neck.
Posted by: Nathan Galli