SCI Publications
2008
T. Preusser, H. Scharr, K. Krajsek, R.M. Kirby.
“Building Blocks for Computer Vision with Stochastic Partial Differential Equations,” In International Journal of Computer Vision, Vol. 80, No. 3, Springer, pp. 375--405. July, 2008.
DOI: 10.1007/s11263-008-0145-5
S. Sharma, S. Vakkalanka, G. Gopalakrishnan, R.M. Kirby, R. Thakur, W. Gropp.
“A Formal Approach to Detect Functionally Irrelevant Barriers in MPI Programs,” In Proceedings of EuroPVM-MPI 2008, Dublin, Ireland, Vol. 5205, pp. 265--273. September, 2008.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-87475-1_36
We examine the unsolved problem of automatically and efficiently detecting functionally irrelevant barriers in MPI programs. A functionally irrelevant barrier is a set of MPI_Barrier calls, one per MPI process, such that their removal does not alter the overall MPI communication structure of the program. Static analysis methods are incapable of solving this problem, as MPI programs can compute many quantities at runtime, including send targets, receive sources, tags, and communicators, and also can have data-dependent control flows. We offer an algorithm called Fib to solve this problem based on dynamic (runtime) analysis. Fib applies to MPI programs that employ 24 widely used two-sided MPI operations. We show that it is sufficient to detect barrier calls whose removal causes a wildcard receive statement placed before or after a barrier to now begin matching a send statement with which it did not match before. Fib determines whether a barrier becomes relevant in any interleaving of the MPI processes of a given MPI program. Since the number of interleavings can grow exponentially with the number of processes, Fib employs a sound method to drastically reduce this number, by computing only the relevant interleavings. We show that many MPI programs do not have data dependent control flows, thus making the results of Fib applicable to all the input data the program can accept.
M. Steffen, S. Curtis, R.M. Kirby, J.K. Ryan.
“Investigation of Smoothness-Increasing Accuracy-Conserving Filters for Improving Streamline Integration Through Discontinuous Fields,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 14, No. 3, pp. 680--692. 2008.
M. Steffen, R.M. Kirby, M. Berzins.
“Analysis and Reduction of Quadrature Errors in the Material Point Method (MPM),” In International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, Vol. 76, No. 6, pp. 922--948. 2008.
DOI: 10.1002/nme.2360
M. Steffen, P.C. Wallstedt, J.E. Guilkey, R.M. Kirby, M. Berzins.
“Examination and Analysis of Implementation Choices within the Material Point Method (MPM),” In Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol. 31, No. 2, pp. 107--127. 2008.
S. Vakkalanka, M. DeLisi, G. Gopalakrishnan, R.M. Kirby, R. Thakur, W. Gropp.
“Implementing Efficient Dynamic Formal Verification Methods for MPI Programs,” In Recent Advances in Parallel Virtual Machine and Message Passing Interface
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Dublin, Ireland, Vol. 5205, pp. 248--256. September, 2008.
We examine the problem of formally verifying MPI programs for safety properties through an efficient dynamic (runtime) method in which the processes of a given MPI program are executed under the control of an interleaving scheduler. To ensure full coverage for given input test data, the algorithm must take into consideration MPI’s out-of-order completion semantics. The algorithm must also ensure that nondeterministic constructs (e.g., MPI wildcard receive matches) are executed in all possible ways. Our new algorithm rewrites wildcard receives to specific receives, one for each sender that can potentially match with the receive. It then recursively explores each case of the specific receives. The list of potential senders matching a receive is determined through a runtime algorithm that exploits MPI’s operation ordering semantics. Our verification tool ISP that incorporates this algorithm efficiently verifies several programs and finds bugs missed by existing informal verification tools.
S. Vakkalanka, M. DeLisi, G. Gopalakrishnan, R.M. Kirby.
“Scheduling Considerations for Building Dynamic Verification Tools for MPI,” In Proceedings of the 6th Workshop on Parallel and Distributed Systems: Testing, Analysis, and Debugging, Seattle, WA, PADTAD '08, Vol. 3, ACM, pp. 1--6. 2008.
ISBN: 978-1-60558-052-4
DOI: 10.1145/1390841.1390844
S. Vakkalanka, G. Gopalakrishnan, R.M. Kirby.
“Dynamic Verification of MPI Programs with Reductions in Presence of Split Operations and Relaxed Orderings,” In Computer Aided Verification Lecture Notes in Computer Science , Vol. 5123, pp. 66--79. July, 2008.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-70545-1_9
Dynamic verification methods are the natural choice for debugging real world programs when model extraction and maintenance are expensive. Message passing programs written using the MPI library fall under this category. Partial order reduction can be very effective for MPI programs because for each process, all its local computational steps, as well as many of its MPI calls, commute with the corresponding steps of all other processes. However, when dependencies arise among MPI calls, they are often a function of the runtime state. While this suggests the use of dynamic partial order reduction (DPOR), three aspects of MPI make previous DPOR algorithms inapplicable: (i) many MPI calls are allowed to complete out of program order; (ii) MPI has global synchronization operations (e.g., barrier) that have a special weak semantics; and (iii) the runtime of MPI cannot, without intrusive modifications, be forced to pursue a specific interleaving because of MPI’s liberal message matching rules, especially pertaining to ‘wildcard receives’. We describe our new dynamic verification algorithm ‘POE’ that exploits the out of order completion semantics of MPI by delaying the issuance of MPI calls, issuing them only according to the formation of match-sets, which are ample ‘big-step’ moves. POE guarantees to manifest any feasible interleaving by dynamically rewriting wildcard receives by specific-source receives. This is the first dynamic model-checking algorithm with reductions for (a large subset of) MPI that guarantees to catch all deadlocks and local assertion violations, and is found to work well in practice.
R.T. Whitaker, R.M. Kirby, J.G. Sinstra, M.D. Meyer.
“Multimaterial Meshing of MRI Head Data for Bioelectric Field Simulations,” In Proceedings of the 17th International Meshing Roundtable, 2008.
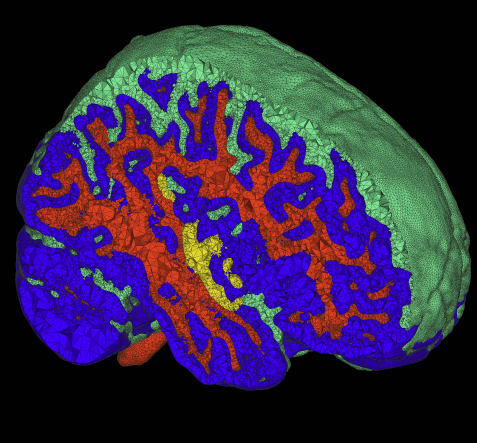
The problem of body fitting meshes that are both adaptive and geometrically accurate is important in a variety of biomedical applications in a multitude of clinical settings, including electrocardiology, neurology, and orthopedics. Adaptivity is necessary because of the combination of large-scale and smallscale structures (e.g. relatively small blood vessels spanning a human head). Geometric accuracy is important for several reasons. In some cases, such as computational fluid dynamics, the fine-scale structure of the fluid domain is important for qualitative and quantitative accuracy of the solutions. More generally, finite element approximations of elliptic problems with rough coefficients require increased spatial resolution normal to material boundaries [3]. The problem of constructing meshes from biomedical images is particularly difficult because of the complexity and irregularity of the structures, and thus tuning or correcting meshes by hand is quite difficult and time consuming. Many researchers and, indeed, commercial products simply subdivide the underlying hexahedral image grid and assign material properties to tetrahedra based on standard decomposition of each hexahedron into tetrahedra.
This paper presents a small case study of the results of a recently developed method for multimaterial, tetrahedral meshing of biomedical volumes [6]. The method uses an iterative relaxation of surface point point positions that are constrained to subsets of the volume that correspond to boundaries between different materials. In this paper we briefly review the method and present results on a set of MRI head images for use in bioelectric field simulation and source localization.
Y. Yang, X. Chen, G. Gopalakrishnan, R.M. Kirby.
“Efficient Stateful Dynamic Partial Order Reduction,” In Proceedings of Model Checking Software: 15th International SPIN Workshop, Los Angeles, CA, Vol. 5156, pp. 288--305. August, 2008.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-85114-1_20
In applying stateless model checking methods to realistic multithreaded programs, we find that stateless search methods are ineffective in practice, even with dynamic partial order reduction (DPOR) enabled. To solve the inefficiency of stateless runtime model checking, this paper makes two related contributions. The first contribution is a novel and conservative light-weight method for storing abstract states at runtime to help avoid redundant searches. The second contribution is a stateful dynamic partial order reduction algorithm (SDPOR) that avoids a potential unsoundness when DPOR is naively applied in the context of stateful search. Our stateful runtime model checking approach combines light-weight state recording with SDPOR, and strikes a good balance between state recording overheads, on one hand, and the elimination of redundant searches, on the other hand. Our experiments confirm the effectiveness of our approach on several multithreaded benchmarks in C, including some practical programs.
2007
S. Curtis, R.M. Kirby, J.K. Ryan, C.-W. Shu.
“Post-Processing for the Discontinuous Galerkin Method Over Non-Uniform Meshes,” In SIAM Journal of Scientific Computing, Vol. 30, No. 1, pp. 272--289. 2007.
S.E. Geneser, R.M. Kirby, D. Xiu, F.B. Sachse.
“Stochastic Markovian Modeling of Electrophysiology of Ion Channels: Reconstruction of Standard Deviations in Macroscopic Currents,” In Journal of Theoretical Biology, Vol. 245, No. 4, pp. 627--637. 2007.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2006.10.016
Markovian models of ion channels have proven useful in the reconstruction of experimental data and prediction of cellular electrophysiology. We present the stochastic Galerkin method as an alternative to Monte Carlo and other stochastic methods for assessing the impact of uncertain rate coefficients on the predictions of Markovian ion channel models. We extend and study two different ion channel models: a simple model with only a single open and a closed state and a detailed model of the cardiac rapidly activating delayed rectifier potassium current. We demonstrate the efficacy of stochastic Galerkin methods for computing solutions to systems with random model parameters. Our studies illustrate the characteristic changes in distributions of state transitions and electrical currents through ion channels due to random rate coefficients. Furthermore, the studies indicate the applicability of the stochastic Galerkin technique for uncertainty and sensitivity analysis of bio-mathematical models.
Keywords: Stochastic Galerkin, Polynomial chaos, Stochastic processes, Markov modeling, Ion channels
C.W. Hamman, R.M. Kirby, M. Berzins.
“Parallelization and Scalability of a Spectral Element Channel Flow Solver for Incompressible Navier-Stokes Equations,” In Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, Vol. 14, No. 10, pp. 1403--1422. 2007.
C.R. Hamman, R.M. Kirby, M. Berzins.
“Parallel Direct Simulation of Incompressible Navier Stokes Equations,” In Concurrency and Computation, Vol. 19, No. 10, pp. 1403-1427. 2007.
R.M. Kirby, Z. Yosibash, G.E. Karniadakis.
“Towards Stable Coupling Methods for High-Order Discretizations of Fluid-Structure Interaction: Algorithms and Observations,” In Journal of Computational Physics, Vol. 223, No. 2, pp. 489--518. 2007.
M.D. Meyer, B. Nelson, R.M. Kirby, R.T. Whitaker.
“Particle Systems for Efficient and Accurate Finite Element Visualization,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 13, No. 5, pp. 1015--1026. 2007.
M.D. Meyer, R.M. Kirby, R.T. Whitaker.
“Topology, Accuracy, and Quality of Isosurface Meshes Using Dynamic Particles,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 13, No. 6, IEEE, pp. 1704--1711. Nov, 2007.
E.P. Newren, A.L. Fogelson, R.D. Guy, R.M. Kirby.
“Unconditionally Stable Discretizations of the Immersed Boundary Equations,” In Journal of Computational Physics, Vol. 222, No. 2, pp. 702--719. 2007.
E.P. Newren, A.L. Fogelson, R.D. Guy, R.M. Kirby.
“Unconditionally Stable Discretizations of the Immersed Boundary Equations,” In Journal of Computational Physics, Vol. 222, No. 2, pp. 702--719. March, 2007.
T. Ochotta, C.E. Scheidegger, J. Schreiner, Y. Lima, R.M. Kirby, C.T. Silva.
“A Unified Projection Operator for Moving Least Squares Surfaces,” SCI Institute Technical Report, No. UUSCI-2007-006, University of Utah, 2007.
Page 7 of 10
