SCI Publications
2011
T. Fogal, J. Krüger.
“Efficient I/O for Parallel Visualization,” In Proceedings of the Eurographics Symposium on Parallel Graphics and Visualization (2011), Edited by T. Kuhlen and R. Pajarola and K. Zhou, pp. 81--90. 2011.
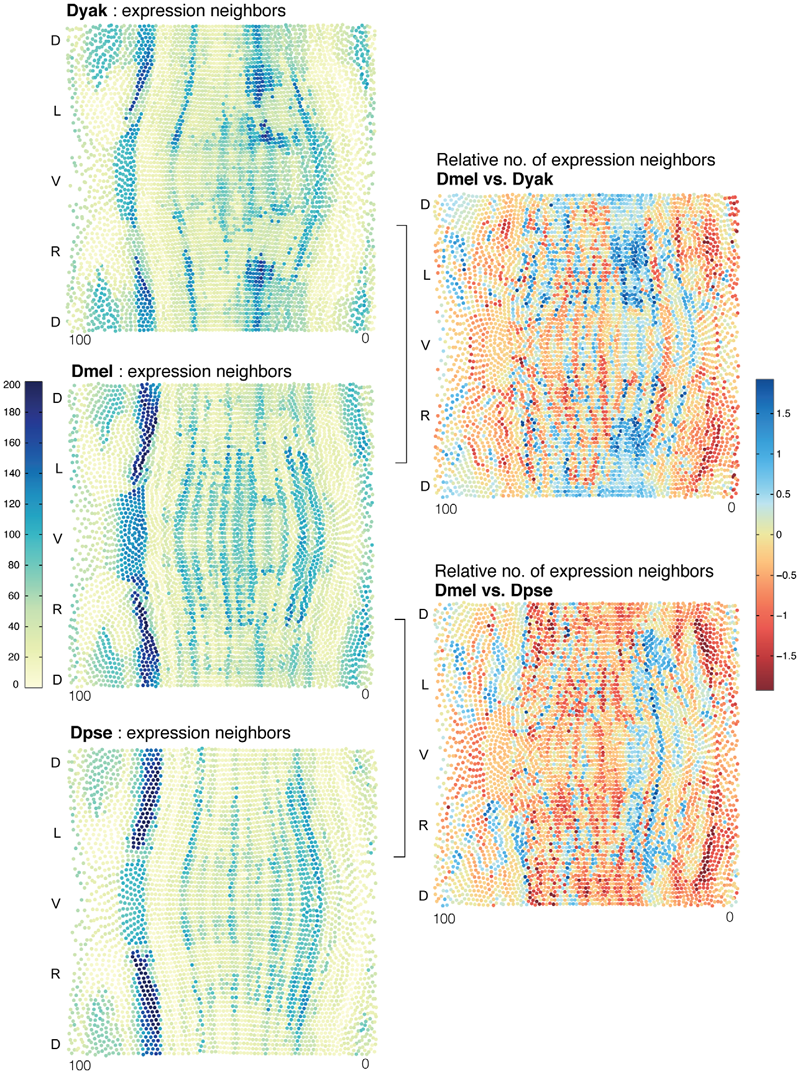
C. Fowlkes, K. Eckenrode, M. Bragdon, M.D. Meyer, Z. Wunderlich, L. Simirenko, C. Luengo, S. Keranen, C. Henriquez, D. Knowles, M. Biggin, M. Eisen, A. DePace.
“A Conservered Developmental Patterning Network Produces Quantitatively Different Output in Multiple Species of Drosophila,” In PLoS Genetics, Vol. 7, No. 10:e1002346, pp. 17 pages. October, 2011.
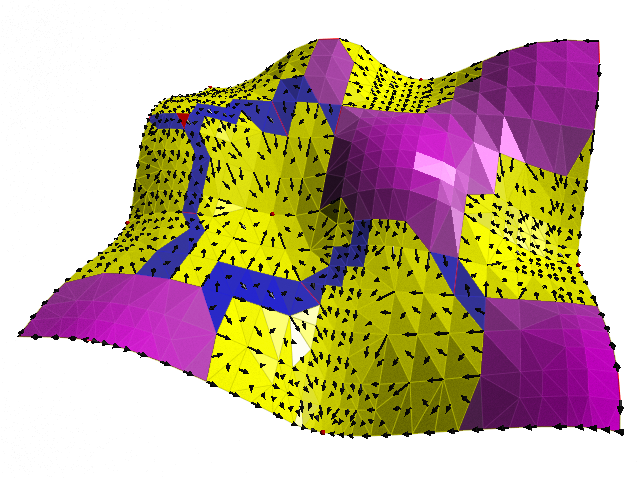
Z. Fu, W.-K. Jeong, Y. Pan, R.M. Kirby, R.T. Whitaker.
“A fast iterative method for solving the Eikonal equation on triangulated surfaces,” In SIAM Journal of Scientific Computing, Vol. 33, No. 5, pp. 2468--2488. 2011.
DOI: 10.1137/100788951
PubMed Central ID: PMC3360588
This paper presents an efficient, fine-grained parallel algorithm for solving the Eikonal equation on triangular meshes. The Eikonal equation, and the broader class of Hamilton–Jacobi equations to which it belongs, have a wide range of applications from geometric optics and seismology to biological modeling and analysis of geometry and images. The ability to solve such equations accurately and efficiently provides new capabilities for exploring and visualizing parameter spaces and for solving inverse problems that rely on such equations in the forward model. Efficient solvers on state-of-the-art, parallel architectures require new algorithms that are not, in many cases, optimal, but are better suited to synchronous updates of the solution. In previous work [W. K. Jeong and R. T. Whitaker, SIAM J. Sci. Comput., 30 (2008), pp. 2512–2534], the authors proposed the fast iterative method (FIM) to efficiently solve the Eikonal equation on regular grids. In this paper we extend the fast iterative method to solve Eikonal equations efficiently on triangulated domains on the CPU and on parallel architectures, including graphics processors. We propose a new local update scheme that provides solutions of first-order accuracy for both architectures. We also propose a novel triangle-based update scheme and its corresponding data structure for efficient irregular data mapping to parallel single-instruction multiple-data (SIMD) processors. We provide detailed descriptions of the implementations on a single CPU, a multicore CPU with shared memory, and SIMD architectures with comparative results against state-of-the-art Eikonal solvers.
S.E. Geneser, J.D. Hinkle, R.M. Kirby, Bo Wang, B. Salter, S. Joshi.
“Quantifying variability in radiation dose due to respiratory-induced tumor motion,” In Medical Image Analysis, Vol. 15, No. 4, pp. 640--649. 2011.
DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2010.07.003
G. Gerig, I. Oguz, S. Gouttard, J. Lee, H. An, W. Lin, M. McMurray, K. Grewen, J. Johns, M.A. Styner.
“Synergy of image analysis for animal and human neuroimaging supports translational research on drug abuse,” In Frontiers in Child and Neurodevelopmental Psychiatry, Vol. 2, Edited by Linda Mayes, pp. 9 pages. 2011.
ISSN: 1664-0640
DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2011.00053
G. Gerig, J.H. Gilmore, W. Lin.
“Brain Maturation of Newborns and Infants,” Encyclopedia on Early Childhood Development (online): Brain Development in Children - According to Experts, Montreal, Quebec, Centre of Excellence for Early Childhood Development and Strategic Knowledge Cluster on Early Child Development, pp. 1--6. 2011.
Recently, imaging studies of early human development have received more attention, as improved modeling methods might lead to a clearer understanding of the origin, timing, and nature of differences in neurodevelopmental disorders. Non-invasive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide three-dimensional images of the infant brain in less than 20 minutes, with unprecedented anatomical details and contrast of brain anatomy, cortical and subcortical structures and brain connectivity. Repeating MRI at different stages of development, e.g., in yearly intervals starting after birth, gives scientists the opportunity to study the trajectory of brain growth and compare individual growth trajectories to normative models. These comparisons become highly relevant in personalized medicine, where early diagnosis is a critical juncture for timing and therapy types.
T. Geymayer, A. Lex, M. Streit, D. Schmalstieg.
“Visualizing the Effects of Logically Combined Filters,” In Proceedings of the Conference on Information Visualisation (IV '11), IEEE, pp. 47--52. 2011.
Filtering data is an essential process in a drill-down analysis of large data sets. Filtering can be necessary for several reasons. The main objective for filters is to uncover the relevant subsets of a dataset. Another, equally relevant goal is to reduce a dataset to dimensions to which either visualization or algorithmic analysis techniques scale. However, with multiple filters applied and possibly even logically combined, it becomes difficult for users to judge the effects of a filter chain. In this paper we present a simple, yet effective way to interactively visualize a sequence of filters and logical combinations of these. Such a visualized filter-pipeline allows analysts to easily judge the effect of every single filter and also their combination on the data set under investigation and therefore, leads to a faster and more efficient workflow.
We also present an implementation of the proposed technique in an information visualization framework for the life sciences. The technique, however, could be employed in many other information visualization contexts as well.
G. Gopalakrishnan, R.M. Kirby, S. Siegel, R. Thakur, W. Gropp, E. Lusk, B.R. de Supinski, M. Schultz, G. Bronevetsky.
“Formal Analysis of MPI-Based Parallel Programs: Present and Future,” In Communications of the ACM, pp. (accepted). 2011.
J. Grueninger, H. Hoffman, U. Kloos, J. Krüger.
“Multi-Resolution-Display System for Virtual Reality Setups,” In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, HCI International, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 6779/2011, pp. 180--189. 2011.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-21716-6_19

Most large-area video projection systems offer only limited spacial resolution. Consequently, images of detailed scenery cannot be displayed at full fidelity. A possible but significantly more costly strategy is a tiled projection display. If this solution is not feasible then either aliasing occurs or some anti-aliasing method is used at the cost of reduced scene quality.
In this paper we describe a novel cost effective multi-resolution display system. It allows users to select any part of a stereoscopic projection and view it in significantly higher resolution than possible with the standard projection alone. To achieve this, a pair of video projectors, which can be moved by stepper motors, project a high-resolution inset into a small portion of the low-resolution image. To avoid crosstalk between the low and high resolution projections, a mask is rendered into the low resolution scene to black out the area on the screen that is covered by the inlay.
To demonstrate the effectiveness of our multi-resolution display setup it has been integrated into a number of real life scenarios: a virtual factory, an airplane cabin simulation, and a focus and context volume visualization application (see Figure 1).
Attila Gyulassy, J.A. Levine, V. Pascucci.
“Visualization of Discrete Gradient Construction (Multimedia submission),” In Proceedings of the 27th Symposium on Computational Geometry, Paris, France, ACM, pp. 289--290. June, 2011.
DOI: 10.1145/1998196.1998241
L.K. Ha, J. Krüger, J. Comba, S. Joshi, C.T. Silva.
“Optimal Multi-Image Processing Streaming Framework on Parallel Heterogeneous Systems,” In Proceedings of Eurographics Symposium on Parallel Graphics and Visualization 2011, Note: Awarded Best Paper!, pp. 1--10. 2011.
DOI: 10.2312/EGPGV/EGPGV11/001-010
Atlas construction is an important technique in medical image analysis that plays a central role in understanding the variability of brain anatomy. The construction often requires applying image processing operations to multiple images (often hundreds of volumetric datasets), which is challenging in computational power as well as memory requirements. In this paper we introduce MIP, a Multi-Image Processing streaming framework to harness the processing power of heterogeneous CPU/GPU systems. In MIP we introduce specially designed streaming algorithms and data structures that provides an optimal solution for out-of-core multi-image processing problems both in terms of memory usage and computational efficiency. MIP makes use of the asynchronous execution mechanism supported by parallel heterogeneous systems to efficiently hide the inherent latency of the processing pipeline of out-of-core approaches. Consequently, with computationally intensive problems, the MIP out-of-core solution could achieve the same performance as the in-core solution. We demonstrate the efficiency of the MIP framework on synthetic and real datasets.
L.K. Ha, M.W. Prastawa, G. Gerig, J.H. Gilmore, C.T. Silva.
“Efficient Probabilistic and Geometric Anatomical Mapping Using Particle Mesh Approximation on GPUs,” In International Journal of Biomedical Imaging, Special Issue in Parallel Computation in Medical Imaging Applications, Vol. 2011, Note: Article ID 572187, pp. 16 pages. 2011.
DOI: 10.1155/2011/572187
L.K. Ha, J. Krüger, S. Joshi, C.T. Silva.
“Multi-scale Unbiased Diffeomorphic Atlas Construction on Multi-GPUs,” Vol. 1, Ch. 10, Morgan Kaufmann, pp. 42. 2011.
X. Hao, R.T. Whitaker, P.T. Fletcher.
“Adaptive Riemannian Metrics for Improved Geodesic Tracking of White Matter,” In Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI), Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS), Vol. 6801/2011, pp. 13--24. 2011.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-22092-0_2
D.E. Hart, M. Berzins, C.E. Goodyer, P.K. Jimack.
“Using Adjoint Error Estimation Techniques for Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Line Contact Problems,” In International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, Vol. 67, Note: Published online 29 October, pp. 1559--1570. 2011.
H.C. Hazlett, M. Poe, G. Gerig, M. Styner, C. Chappell, R.G. Smith, C. Vachet, J. Piven.
“Early Brain Overgrowth in Autism Associated with an Increase in Cortical Surface Area Before Age 2,” In Arch of Gen Psych, Vol. 68, No. 5, pp. 467--476. 2011.
DOI: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.39
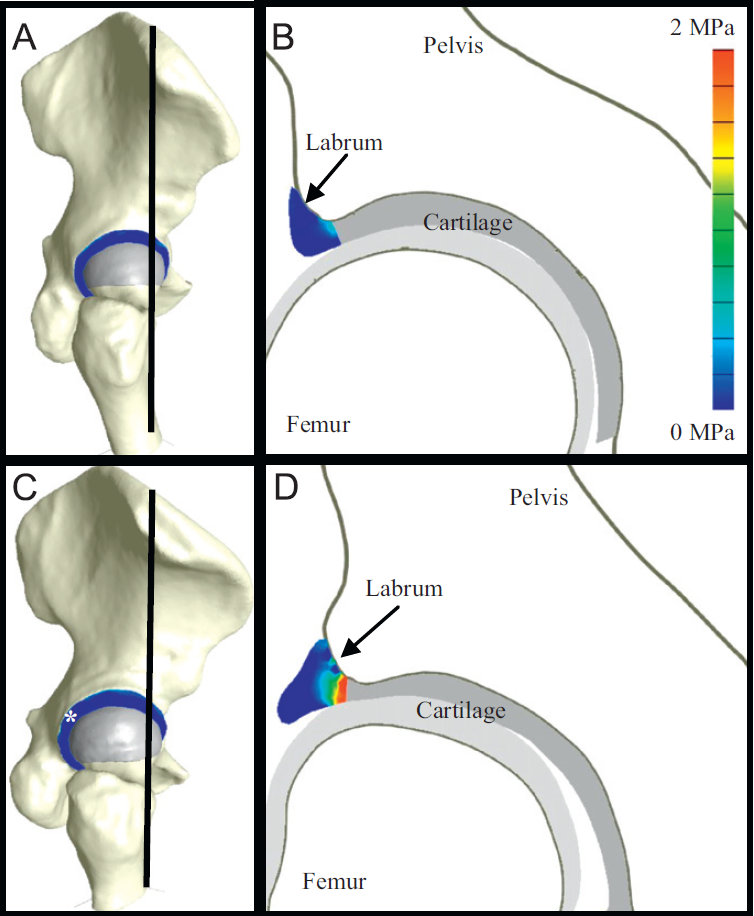
C.R. Henak, B.J. Ellis, M.D. Harris, A.E. Anderson, C.L. Peters, J.A. Weiss.
“Role of the acetabular labrum in load support across the hip joint,” In Journal of Biomechanics, Vol. 44, No. 12, pp. 2201-2206. 2011.
L. Hogrebe, A. Paiva, E. Jurrus, C. Christensen, M. Bridge, J.R. Korenberg, T. Tasdizen.
“Trace Driven Registration of Neuron Confocal Microscopy Stacks,” In IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp. 1345--1348. 2011.
DOI: 10.1109/ISBI.2011.5872649
A. Irimia, M.C. Chambers, J.R. Alger, M. Filippou, M.W. Prastawa, Bo Wang, D. Hovda, G. Gerig, A.W. Toga, R. Kikinis, P.M. Vespa, J.D. Van Horn.
“Comparison of acute and chronic traumatic brain injury using semi-automatic multimodal segmentation of MR volumes,” In Journal of Neurotrauma, Vol. 28, No. 11, pp. 2287--2306. November, 2011.
DOI: 10.1089/neu.2011.1920
PubMed ID: 21787171
Although neuroimaging is essential for prompt and proper management of traumatic brain injury (TBI), there is a regrettable and acute lack of robust methods for the visualization and assessment of TBI pathophysiology, especially for of the purpose of improving clinical outcome metrics. Until now, the application of automatic segmentation algorithms to TBI in a clinical setting has remained an elusive goal because existing methods have, for the most part, been insufficiently robust to faithfully capture TBI-related changes in brain anatomy. This article introduces and illustrates the combined use of multimodal TBI segmentation and time point comparison using 3D Slicer, a widely-used software environment whose TBI data processing solutions are openly available. For three representative TBI cases, semi-automatic tissue classification and 3D model generation are performed to perform intra-patient time point comparison of TBI using multimodal volumetrics and clinical atrophy measures. Identification and quantitative assessment of extra- and intra-cortical bleeding, lesions, edema, and diffuse axonal injury are demonstrated. The proposed tools allow cross-correlation of multimodal metrics from structural imaging (e.g., structural volume, atrophy measurements) with clinical outcome variables and other potential factors predictive of recovery. In addition, the workflows described are suitable for TBI clinical practice and patient monitoring, particularly for assessing damage extent and for the measurement of neuroanatomical change over time. With knowledge of general location, extent, and degree of change, such metrics can be associated with clinical measures and subsequently used to suggest viable treatment options.
Keywords: namic
B.M. Isaacson, J.G. Stinstra, R.D. Bloebaum, COL P.F. Pasquina, R.S. MacLeod.
“Establishing Multiscale Models for Simulating Whole Limb Estimates of Electric Fields for Osseointegrated Implants,” In IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, Vol. 58, No. 10, pp. 2991--2994. 2011.
DOI: 10.1109/TBME.2011.2160722
PubMed ID: 21712151
PubMed Central ID: PMC3179554
Page 60 of 144
