Six New Projects Funded
Anna Busatto receives Pac-12 Scholarship
 Anna Busatto has been named a recipient of the 2022 Pac-12 Postgraduate Scholarship.
Anna Busatto has been named a recipient of the 2022 Pac-12 Postgraduate Scholarship.The scholarship is worth $9,000 and annually recognizes up to two student-athletes from each Pac-12 school. Established in 1999, the award honors and financially assists some of the Conference's most outstanding athletes and scholars as they continue their educations and prepare for careers in their chosen industries. Across the Pac-12, scholarship recipients maintained a minimum 3.0 grade-point average and demonstrated a commitment to education, campus and community involvement, and leadership.
SCI Welcomes Five New Faculty to the Institute
Bei Wang Receives U SEED2SOIL Grant
 SEED2SOIL: Telematic Data for Fleet Vehicles: A Data-Driven Solution Towards Optimal Fleet Management and Clean Vehicle Adoption
SEED2SOIL: Telematic Data for Fleet Vehicles: A Data-Driven Solution Towards Optimal Fleet Management and Clean Vehicle Adoption
Assessing the performance of fleet services has long been an important yet challenging issue for public agencies and researchers. Performance evaluation can help the campus facilities division identify underperforming services, plan for potential investments, justify the previous investments, consolidate across multiple services, and communicate accomplishments and challenges. The goal of this study is to use telematics data to analyze the performance of the fleet operation systems and develop strategic solutions for effective fleet service management. The team will utilize a combination of Geographical Information System (GIS), data science, and visualization methods to identify the underutilized fleet and service coverage gaps, and inform strategic decision-making related to consolidated services and zero-emission vehicle deployment. This will be a joint project between PI Xiaoyue Cathy Liu at the Civil And Environmental Engineering and Co-PI Bei Wang Phillips from the SCI Institute. Through the SEED2SOIL program (https://attheu.utah.edu/facultystaff/sustainability-research-grants/), researchers use the University of Utah Campus as a Living Lab to improve campus operations and contribute to broader sustainability knowledge.
Parashar Named Presidential Professor
 School of Computing professor Manish Parashar, who is the director of the University of Utah’s Scientific Computing and Imaging Institute, was recently named Presidential Professor.
School of Computing professor Manish Parashar, who is the director of the University of Utah’s Scientific Computing and Imaging Institute, was recently named Presidential Professor.The title of Presidential Professor is reserved for those with achievements that “exemplify the highest goals of scholarship as demonstrated by recognition accorded to them from peers with national and international stature and whose record includes evidence of a high dedication to teaching.”
reVISit: Scalable Empirical Evaluation of Interactive Visualizations
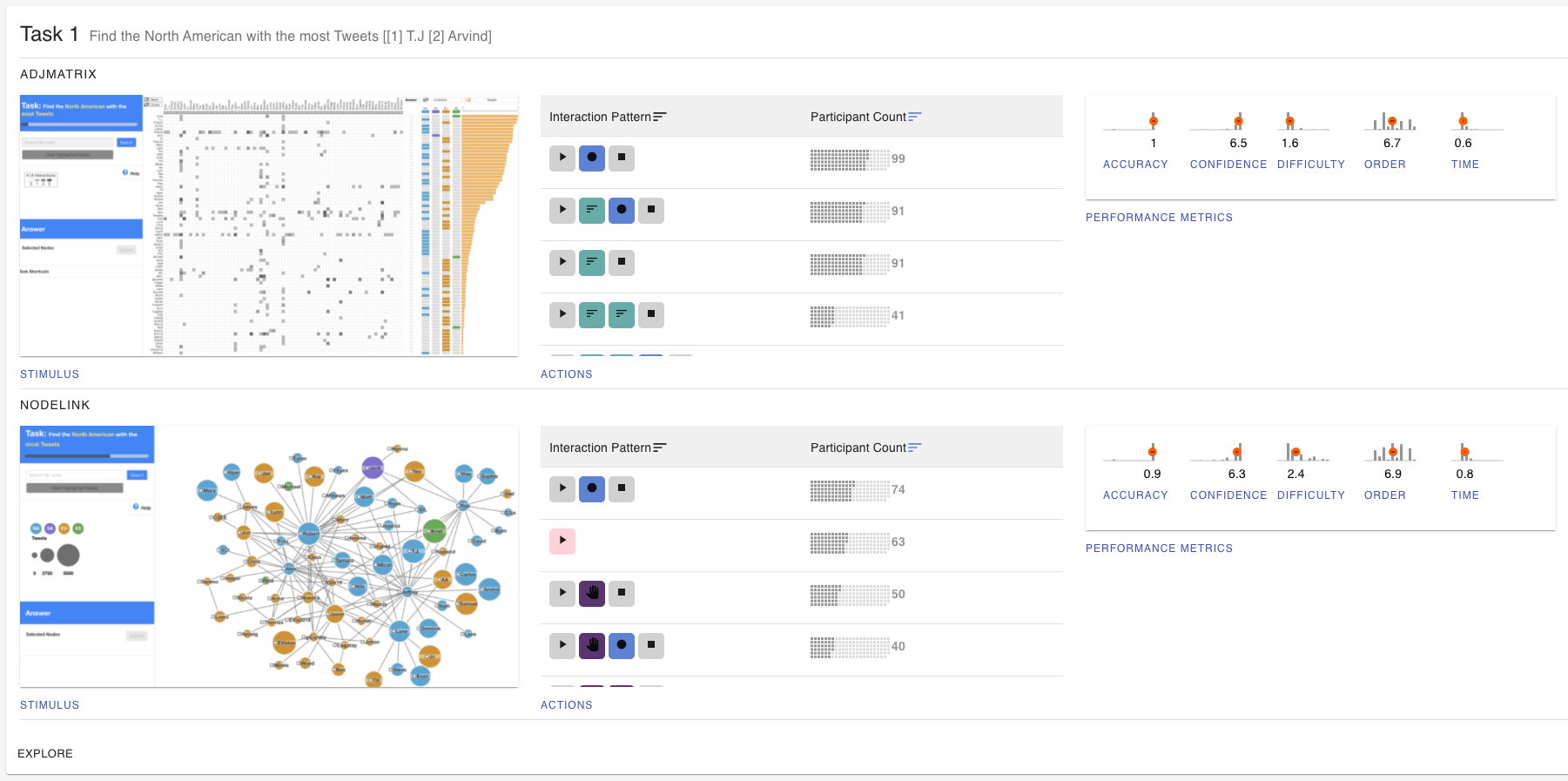 Congratulations to Alex Lex on his NSF award from the CISE Community Research Infrastructure program titled “reVISit: Scalable Empirical Evaluation of Interactive Visualizations". The project is in collaboration with WPI and the University of Toronto.
Congratulations to Alex Lex on his NSF award from the CISE Community Research Infrastructure program titled “reVISit: Scalable Empirical Evaluation of Interactive Visualizations". The project is in collaboration with WPI and the University of Toronto.Bei Wang Wins NSF Career Award
 Congratulations to Bei Wang on her NSF career award. A Measure Theoretic Framework for Topology-Based Visualization. Data generated from multiphysics simulations, such as binary black hole mergers and fluid dynamics, has experienced exponential growth thanks to the growing capabilities of computing facilities. At the same time, data-intensive science relies on the acquisition, management, analysis, and visualization of data with increasing spatial and temporal resolutions. This project develops a new set of approaches to support the core tasks in scientific data visualization (such as feature tracking, event detection, ensemble analysis, and interactive visualization) in a way that is more reflective of the underlying physics using measure theory. The results will be instantiated by a collection of open-source software tools to be deployed for the collaborating scientists in materials science and high-performance computing, and the larger research community. This project leverages tools from geometric measure theory, information theory, and transportation theory for topology-based visualization, which utilizes topological concepts to describe, reduce and organize data for scientific understanding and communication.
Congratulations to Bei Wang on her NSF career award. A Measure Theoretic Framework for Topology-Based Visualization. Data generated from multiphysics simulations, such as binary black hole mergers and fluid dynamics, has experienced exponential growth thanks to the growing capabilities of computing facilities. At the same time, data-intensive science relies on the acquisition, management, analysis, and visualization of data with increasing spatial and temporal resolutions. This project develops a new set of approaches to support the core tasks in scientific data visualization (such as feature tracking, event detection, ensemble analysis, and interactive visualization) in a way that is more reflective of the underlying physics using measure theory. The results will be instantiated by a collection of open-source software tools to be deployed for the collaborating scientists in materials science and high-performance computing, and the larger research community. This project leverages tools from geometric measure theory, information theory, and transportation theory for topology-based visualization, which utilizes topological concepts to describe, reduce and organize data for scientific understanding and communication.
Best Paper Award at PASC22
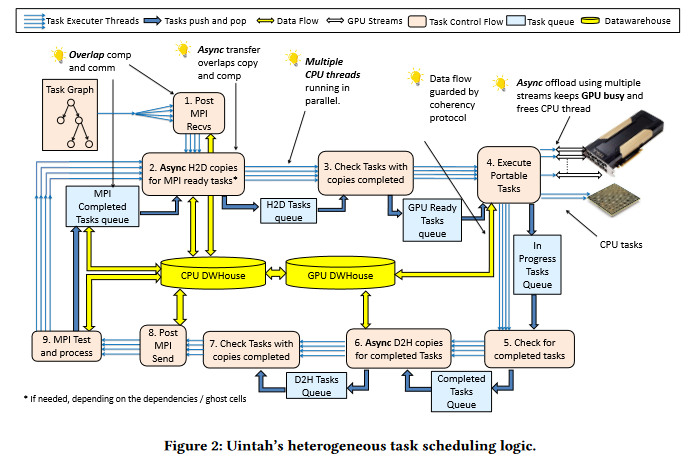 Congratulations to John Holmen, Damodar Sahasrabudhe and Martin Berzins for their best paper award at PASC22.
Congratulations to John Holmen, Damodar Sahasrabudhe and Martin Berzins for their best paper award at PASC22. J.K. Holmen, D. Sahasrabudhe, M. Berzins. “Porting Uintah to Heterogeneous Systems,” In Proceedings of the Platform for Advanced Scientific Computing Conference (PASC22), ACM, 2022.
MRgFUS: A tissue viability imaging biomarker for use in non-invasive breast cancer therapy
 Congratulations to Sarang Joshi and Allison Payne on their five year funding for “A tissue viability imaging biomarker for use in non-invasive breast cancer therapy.” This collaborative project is between the Scientific Computing and Imaging (SCI) Institute and the Utah Center for Advanced Imaging Research (UCAIR).
Congratulations to Sarang Joshi and Allison Payne on their five year funding for “A tissue viability imaging biomarker for use in non-invasive breast cancer therapy.” This collaborative project is between the Scientific Computing and Imaging (SCI) Institute and the Utah Center for Advanced Imaging Research (UCAIR).More women are diagnosed with breast cancer than any other type of cancer, besides skin cancer. This year, an estimated 281,550 women in the United States will be diagnosed with invasive breast cancer, and 49,290 women will be diagnosed with non-invasive (in situ) breast cancer. From 2008 to 2017, invasive breast cancer in women increased by half a percent each year.
Best Paper Awarded at IEEE Pacific Visualization 2022
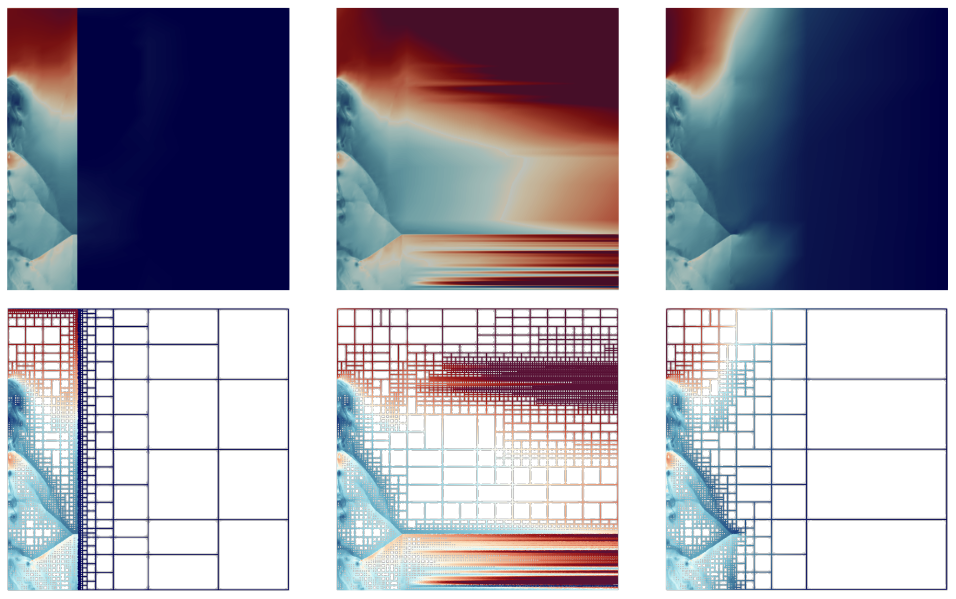 Congratulations to Harsh Bhatia (LLNL/SCI Alumnus), Duong Hoang (SCI), Nathan Morrical (SCI), Peter Lindstrom (LLNl), Peer-Timo Bremer (LLNL/SCI), and Valerio Pascucci (SCI) for receiving the Best Paper Award at the IEEE Pacific Visualization 2022 Conference for their paper:
Congratulations to Harsh Bhatia (LLNL/SCI Alumnus), Duong Hoang (SCI), Nathan Morrical (SCI), Peter Lindstrom (LLNl), Peer-Timo Bremer (LLNL/SCI), and Valerio Pascucci (SCI) for receiving the Best Paper Award at the IEEE Pacific Visualization 2022 Conference for their paper:AMM: Adaptive Multilinear Meshes
