SCI Publications
2007
M. Berzins.
“Is there Still More to Science than Computation?,” In Computing in Science and Engineering, Vol. 9, No. 1, pp. 98--101. 2007.
M. Berzins.
“Adaptive Polynomial Interpolation on Evenly Spaced Meshes.,” In SIAM Review, Vol. 49, No. 4, pp. 604-627. 2007.
E.W. Bethel, C.R. Johnson, K. Joy, S. Ahern, V. Pascucci, H. Childs, J. Cohen, M. Duchaineau, B. Hamann, C.D. Hansen, D. Laney, P. Lindstrom, J. Meredith, G. Ostrouchov, S.G. Parker, C.T. Silva, A.R. Sanderson, X. Tricoche.
“SciDAC Visualization and Analytics Center for Enabling Technology,” In Journal of Physics, Conference Series, Vol. 78, No. 012032, pp. (published online). 2007.
E.W. Bethel, C.R. Johnson, C. Aragon, Prabhat, O. Rübel, G. Weber, V. Pascucci, H. Childs, P.-T. Bremer, B. Whitlock, S. Ahern, J. Meredith, G. Ostrouchov, K. Joy, B. Hamann, C. Garth, M. Cole, C.D. Hansen, S.G. Parker, A.R. Sanderson, C.T. Silva, X. Tricoche.
“DOE's SciDAC Visualization and Analytics Center for Enabling Technologies - Strategy for Petascale Visual Data Analysis Success,” In CTWatch Quarterly, Vol. 3, No. 4, 2007.
S. Boulos, D. Edwards, J.D. Lacewell, J. Kniss, J. Kautz, I. Wald, P. Shirley.
“Packet-based Whitted and Distribution Ray Tracing,” In Proceedings of Graphics Interface 2007, Vol. 234, pp. 177--184. 2007.
P.-T. Bremer, E.M. Bringa, M.A. Duchaineau, A. Gyulassy, D. Laney, A. Mascarenhas, V. Pascucci.
“Topological Feature Extraction and Tracking,” In Proceedings of SciDAC 2007 -- Scientific Discovery Through Advanced Computing, Boston, MA, USA, Vol. 78, Journal of Physics Conference Series, pp. 012032 (5pp). June, 2007.
P.-T. Bremer, V. Pascucci.
“A Practical Approach to Two-Dimensional Scalar Topology,” In Mathematics and Visualization, Springer Verlag, pp. 151--169. 2007.
ISBN: Online ISBN 978-3-540-70823-0 Series Title Mathematics and Visualization Series ISSN 1
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-70823-0_11
Computing and analyzing the topology of scalar fields has proven to be a powerful tool in a wide variety of applications. In recent years the field has evolved from computing contour trees of two-dimensional functions to Reeb graphs of general two-manifolds, analyzing the topology of time-dependent volumes, and finally to creating Morse-Smale complexes of two and three dimensional functions. However, apart from theoretical advances practical applications depend on the development of robust and easy to implement algorithms. The progression from initial to practical algorithms is evident, for example, in the contour tree computation where the latest algorithms consist of no more than a couple of dozens lines of pseudo-code. In this paper we describe a similarly simple approach to compute progressive Morse-Smale complexes of functions over two-manifolds. We discuss compact and transparent data-structures used to compute and store Morse-Smale complexes and demonstrate how they can be used to implement interactive topology based simplification. In particular, we show how special cases arising, for example, from manifolds with boundaries or highly quantized functions are handled effectively. Overall the new algorithm is easier to implement and more efficient both run-time and storage wise than previous approaches by avoiding to refine a given triangulation.
D.H. Brooks, A. Keely, A. Ghodrati, G. Tadmor, R.S. MacLeod.
“Some Spatio-Temporal Approaches to Inverse Electrocardiography,” In Proc. Asilomar Conf. on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, November, 2007.
DOI: 10.1109/ACSSC.2007.4487316
L. Butler, A.J. Stephens.
“Bullet Ray Vision,” In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Interactive Ray Tracing, pp. 167--170. 2007.
C.R. Butson, C.C. McIntyre.
“Differences among implanted pulse generator waveforms cause variations in the neural response to deep brain stimulation,” In Clinical Neurophysiology, Vol. 118, pp. 1889--1894. August, 2007.
ISSN: 1388-2457
DOI: 10.1016/j.clinph.2007.05.061
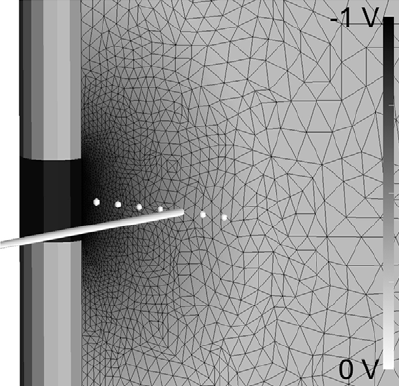
METHODS: We recorded waveforms from a broad range of stimulation parameter settings in each IPG model, and compared them to idealized waveforms that adhered to the parameters specified in the programming device. We then used a previously published computational model to predict the neural response to the various stimulation waveforms.
RESULTS: The stimulation waveforms produced by the IPGs differed from the idealized waveforms assumed in previous theoretical and clinical studies, and the waveforms differed among the IPG models. These differences were greater at higher frequencies and longer pulse widths, and caused variations of up to 0.4 V in activation thresholds for model axons located 3 mm from the DBS electrode contact.
CONCLUSIONS: The specific details of the stimulation waveform directly affect the neural response to DBS and should be accounted for in theoretical and experimental studies of DBS.
SIGNIFICANCE: While the clinical selection of DBS parameters is individualized to each patient based on behavioral outcomes, scientific analysis of stimulation parameter settings and clinical threshold measurements are subject to a previously unrecognized source of error unless the actual waveforms produced by the IPG are accounted for.
C.R. Butson, S.E. Cooper, J.M. Henderson, C.C. McIntyre.
“Patient-specific analysis of the volume of tissue activated during deep brain stimulation,” In NeuroImage, Vol. 34, No. 2, pp. 661--670. January, 2007.
ISSN: 1053-8119
DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.09.034
PubMed ID: 17113789
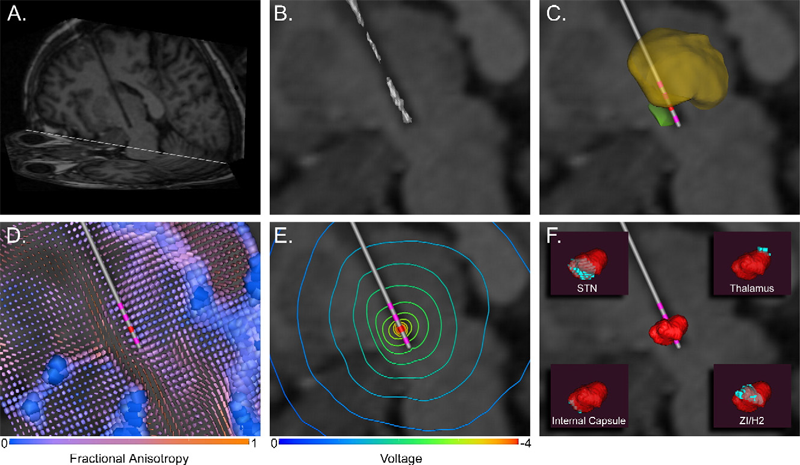
Keywords: Deep Brain Stimulation, Finite Element Analysis, Humans, Imaging, Three-Dimensional, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Models, Neurological, Parkinson Disease, Parkinson Disease: therapy, Pyramidal Tracts, Pyramidal Tracts: physiology, Subthalamic Nucleus, Subthalamic Nucleus: physiology
M. Callahan, M.J. Cole, J.F. Shepherd, J.G. Stinstra, C.R. Johnson.
“BioMesh3D: A Meshing Pipeline for Biomedical Models,” SCI Institute Technical Report, No. UUSCI-2007-009, University of Utah, 2007.
M. Callahan, M.J. Cole, J.F. Shepherd, J.G. Stinstra, C.R. Johnson.
“A Meshing Pipeline for Biomedical Computing,” In Engineering with Computers, Special Issue on Computational Bioengineering, pp. (in press). 2007.
S.P. Callahan, L. Bavoil, V. Pascucci, C.T. Silva.
“Progressive Volume Rendering of Large Unstructured Grids,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 13, No. 1, pp. 1307-1314. 2007.
C.J. Cascio, G. Gerig, J. Piven.
“Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Application to the Study of the Developing Brain,” In J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry, Vol. 46, No. 2, pp. 213--223. February, 2007.
J. Cates, P.T. Fletcher, M. Styner, M. Shenton, R.T. Whitaker.
“Shape Modeling and Analysis with Entropy-Based Particle Systems,” In Proceedings of Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI) 2007, LNCS 4584, pp. 333--345. 2007.
D. Chisnall, M. Chen, C.D. Hansen.
“Ray-Driven Dynamic Working Set Rendering for Complex Volume Scene Graphs Involving Large Point Clouds,” In The Visual Computer, Vol. 23, No. 3, pp. 167--179. 2007.
S. Curtis, R.M. Kirby, J.K. Ryan, C.-W. Shu.
“Post-Processing for the Discontinuous Galerkin Method Over Non-Uniform Meshes,” In SIAM Journal of Scientific Computing, Vol. 30, No. 1, pp. 272--289. 2007.
K. Damevski, K. Zhang, S.G. Parker.
“Practical Parallel Remote Method Invocation for the Babel Compiler,” In Proceedings of the 2007 Symposium on Component and Framework Technology in High-Performance and Scientific Computing, pp. 131--140. 2007.
K. Damevski, A. Swaminathan, S.G. Parker.
“Highly Scalable Distributed Component Framework for Scientific Computing,” In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communication (HPCC 2007), 2007.
Page 85 of 144
