SCI Publications
2015
M. R. Swanson, J. J. Wolff, J. T. Elison, H. Gu, H. C. Hazlett, K. Botteron, M. Styner, S. Paterson, G. Gerig, J. Constantino, S. Dager, A. Estes, C. Vachet, J. Piven.
“Splenium development and early spoken language in human infants,” In Developmental Science, Wiley Online Library, 2015.
ISSN: 1467-7687
DOI: 10.1111/desc.12360
The association between developmental trajectories of language-related white matter fiber pathways from 6 to 24 months of age and individual differences in language production at 24 months of age was investigated. The splenium of the corpus callosum, a fiber pathway projecting through the posterior hub of the default mode network to occipital visual areas, was examined as well as pathways implicated in language function in the mature brain, including the arcuate fasciculi, uncinate fasciculi, and inferior longitudinal fasciculi. The hypothesis that the development of neural circuitry supporting domain-general orienting skills would relate to later language performance was tested in a large sample of typically developing infants. The present study included 77 infants with diffusion weighted MRI scans at 6, 12 and 24 months and language assessment at 24 months. The rate of change in splenium development varied significantly as a function of language production, such that children with greater change in fractional anisotropy (FA) from 6 to 24 months produced more words at 24 months. Contrary to findings from older children and adults, significant associations between language production and FA in the arcuate, uncinate, or left inferior longitudinal fasciculi were not observed. The current study highlights the importance of tracing brain development trajectories from infancy to fully elucidate emerging brain–behavior associations while also emphasizing the role of the splenium as a key node in the structural network that supports the acquisition of spoken language.
Note: VisTrails: A scientific workflow management system. Scientific Computing and Imaging Institute (SCI), Download from: http://www.vistrails.org, 2015.
I. Wald, A. Knoll, G. P. Johnson, W. Usher, V. Pascucci, M. E. Papka.
“CPU Ray Tracing Large Particle Data with Balanced P-k-d Trees,” In 2015 IEEE Scientific Visualization Conference, IEEE, Oct, 2015.
DOI: 10.1109/scivis.2015.7429492
R. Whitaker, W. Thompson, J. Berger, B. Fischhof, M. Goodchild, M. Hegarty, C. Jermaine, K. S. McKinley, A. Pang, J. Wendelberger.
“Workshop on Quantification, Communication, and Interpretation of Uncertainty in Simulation and Data Science,” Note: Computing Community Consortium, 2015.
Modern science, technology, and politics are all permeated by data that comes from people, measurements, or computational processes. While this data is often incomplete, corrupt, or lacking in sufficient accuracy and precision, explicit consideration of uncertainty is rarely part of the computational and decision making pipeline. The CCC Workshop on Quantification, Communication, and Interpretation of Uncertainty in Simulation and Data Science explored this problem, identifying significant shortcomings in the ways we currently process, present, and interpret uncertain data. Specific recommendations on a research agenda for the future were made in four areas: uncertainty quantification in large-scale computational simulations, uncertainty quantification in data science, software support for uncertainty computation, and better integration of uncertainty quantification and communication to stakeholders.
J. J. Wolff, G. Gerig, J. D. Lewis, T. Soda, M. A. Styner, C. Vachet, K. N. Botteron, J. T. Elison, S. R. Dager, A. M. Estes, H. C. Hazlett, R. T. Schultz, L. Zwaigenbaum, J. Piven.
“Altered corpus callosum morphology associated with autism over the first 2 years of life,” In Brain, 2015.
DOI: 10.1093/brain/awv118

M. Zhang, P. T. Fletcher.
“Finite-Dimensional Lie Algebras for Fast Diffeomorphic Image Registration,” In Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI), 2015.
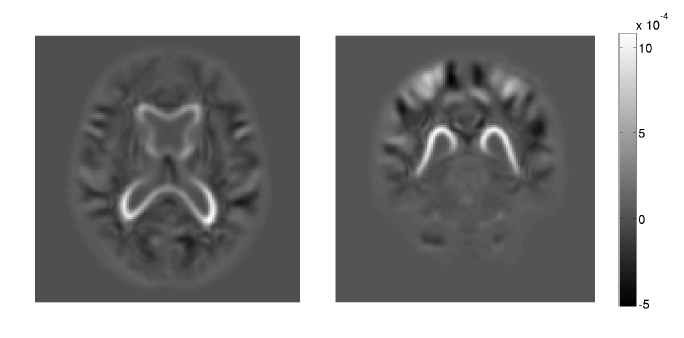
M. Zhang, P. T. Fletcher.
“Bayesian Principal Geodesic Analysis for Estimating Intrinsic Diffeomorphic Image Variability,” In Medical Image Analysis (accepted), 2015.

M. Zhang, H. Shao, P. T. Fletcher.
“A Mixture Model for Automatic Diffeomorphic Multi-Atlas Building,” In MICCAI Workshop, Springer, 2015.
Computing image atlases that are representative of a dataset
is an important first step for statistical analysis of images. Most current approaches estimate a single atlas to represent the average of a large population of images, however, a single atlas is not sufficiently expressive to capture distributions of images with multiple modes. In this paper, we present a mixture model for building diffeomorphic multi-atlases that can represent sub-populations without knowing the category of each observed data point. In our probabilistic model, we treat diffeomorphic image transformations as latent variables, and integrate them out using a Monte Carlo Expectation Maximization (MCEM) algorithm via Hamiltonian Monte Carlo (HMC) sampling. A key benefit of our model is that the mixture modeling inference procedure results in an automatic clustering of the dataset. Using 2D synthetic data generated from known parameters, we demonstrate the ability of our model to successfully recover the multi-atlas and automatically cluster the dataset. We also show the effectiveness of the proposed method in a multi-atlas estimation problem for 3D brain images.
2014
G. Adluru, Y. Gur, J. Anderson, L. Richards, N. Adluru, E. DiBella.
“Assessment of white matter microstructure in stroke patients using NODDI,” In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Int. Conf. Engineering and Biology Society (EMBC), 2014.
Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) is widely used to study changes in white matter following stroke. In various studies employing diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and high angular resolution diffusion imaging (HARDI) modalities, it has been shown that fractional anisotropy (FA), mean diffusivity (MD), and generalized FA (GFA) can be used as measures of white matter tract integrity in stroke patients. However, these measures may be non-specific, as they do not directly delineate changes in tissue microstructure. Multi-compartment models overcome this limitation by modeling DWI data using a set of indices that are directly related to white matter microstructure. One of these models which is gaining popularity, is neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI). This model uses conventional single or multi-shell HARDI data to describe fiber orientation dispersion as well as densities of different tissue types in the imaging voxel. In this paper, we apply for the first time the NODDI model to 4-shell HARDI stroke data. By computing NODDI indices over the entire brain in two stroke patients, and comparing tissue regions in ipsilesional and contralesional hemispheres, we demonstrate that NODDI modeling provides specific information on tissue microstructural changes. We also introduce an information theoretic analysis framework to investigate the non-local effects of stroke in the white matter. Our initial results suggest that the NODDI indices might be more specific markers of white matter reorganization following stroke than other measures previously used in studies of stroke recovery.
S.P. Awate, R.T. Whitaker.
“Multiatlas Segmentation as Nonparametric Regression,” In IEEE Trans Med Imaging, April, 2014.
PubMed ID: 24802528
This paper proposes a novel theoretical framework to model and analyze the statistical characteristics of a wide range of segmentation methods that incorporate a database of label maps or atlases; such methods are termed as label fusion or multiatlas segmentation. We model these multiatlas segmentation problems as nonparametric regression problems in the high-dimensional space of image patches. We analyze the nonparametric estimator's convergence behavior that characterizes expected segmentation error as a function of the size of the multiatlas database. We show that this error has an analytic form involving several parameters that are fundamental to the specific segmentation problem (determined by the chosen anatomical structure, imaging modality, registration algorithm, and labelfusion algorithm). We describe how to estimate these parameters and show that several human anatomical structures exhibit the trends modeled analytically. We use these parameter estimates to optimize the regression estimator. We show that the expected error for large database sizes is well predicted by models learned on small databases. Thus, a few expert segmentations can help predict the database sizes required to keep the expected error below a specified tolerance level. Such cost-benefit analysis is crucial for deploying clinical multiatlas segmentation systems.
S.P. Awate, Y.-Y. Yu, R.T. Whitaker.
“Kernel Principal Geodesic Analysis,” In Proceedings of the European Conference on Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases (ECML PKDD), Springer LNAI, 2014.
Kernel principal component analysis (kPCA) has been proposed as a dimensionality-reduction technique that achieves nonlinear, low-dimensional representations of data via the mapping to kernel feature space. Conventionally, kPCA relies on Euclidean statistics in kernel feature space. However, Euclidean analysis can make kPCA inefficient or incorrect for many popular kernels that map input points to a hypersphere in kernel feature space. To address this problem, this paper proposes a novel adaptation of kPCA, namely kernel principal geodesic analysis (kPGA), for hyperspherical statistical analysis in kernel feature space. This paper proposes tools for statistical analyses on the Riemannian manifold of the Hilbert sphere in the reproducing kernel Hilbert space, including algorithms for computing the sample weighted Karcher mean and eigen analysis of the sample weighted Karcher covariance. It then applies these tools to propose novel methods for (i)~dimensionality reduction and (ii)~clustering using mixture-model fitting. The results, on simulated and real-world data, show that kPGA-based methods perform favorably relative to their kPCA-based analogs.
H. Bhatia, V. Pascucci, R.M. Kirby, P.-T. Bremer.
“Extracting Features from Time-Dependent Vector Fields Using Internal Reference Frames,” In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 33, No. 3, pp. 21--30. June, 2014.
DOI: 10.1111/cgf.12358
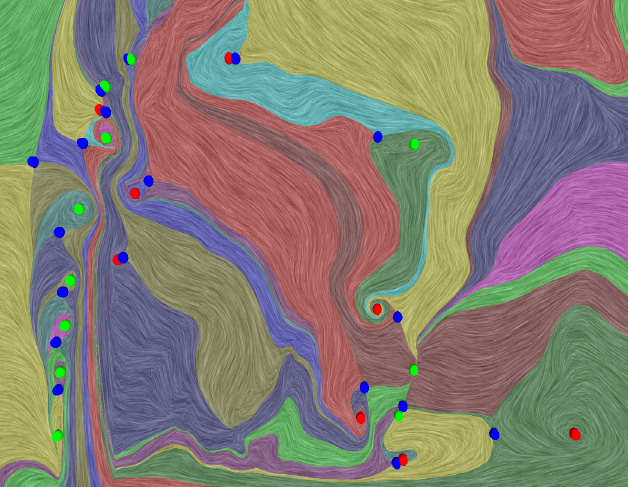
This paper introduces a new data-driven technique to compute internal reference frames for large-scale complex flows. More general than uniformly moving frames, these frames can transform unsteady fields, which otherwise require substantial processing of resources, into a sequence of individual snapshots that can be analyzed using the large body of steady-flow analysis techniques. Our approach is simple, theoretically well-founded, and uses an embarrassingly parallel algorithm for structured as well as unstructured data. Using several case studies from fluid flow and turbulent combustion, we demonstrate that internal frames are distinguished, result in temporally coherent structures, and can extract well-known as well as notoriously elusive features one snapshot at a time.
H. Bhatia, A. Gyulassy, H. Wang, P.-T. Bremer, V. Pascucci .
“Robust Detection of Singularities in Vector Fields,” In Topological Methods in Data Analysis and Visualization III, Mathematics and Visualization, Springer International Publishing, pp. 3--18. March, 2014.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-04099-8_1
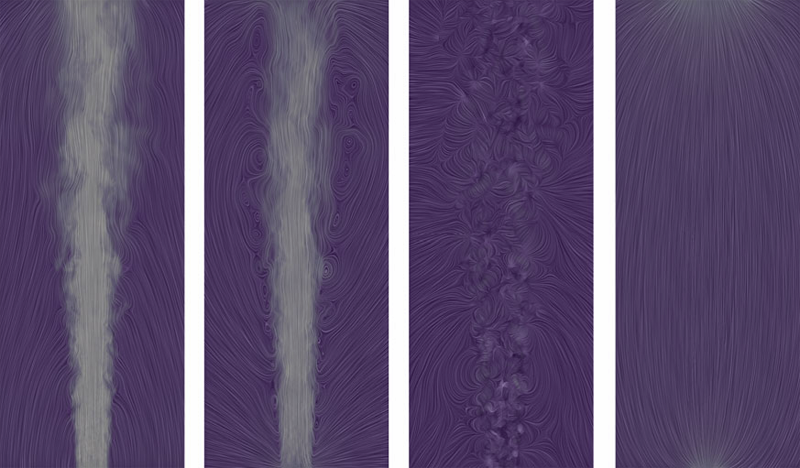
H. Bhatia, V. Pascucci, P.-T. Bremer.
“The Natural Helmholtz-Hodge Decomposition For Open-Boundary Flow Analysis,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG), Vol. 99, pp. 1566--1578. 2014.
DOI: 10.1109/TVCG.2014.2312012

A. Bigelow, S. Drucker, D. Fisher, M.D. Meyer.
“Reflections on How Designers Design With Data,” In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Advanced Visual Interfaces (AVI), Note: Awarded Best Paper!, 2014.
Keywords: Visualization, infographics, design practice
J.J.E. Blauer, D. Swenson, K. Higuchi, G. Plank, R. Ranjan, N. Marrouche,, R.S. MacLeod.
“Sensitivity and Specificity of Substrate Mapping: An In Silico Framework for the Evaluation of Electroanatomical Substrate Mapping Strategies,” In Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, In Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, Vol. 25, No. 7, Note: Featured on journal cover., pp. 774--780. May, 2014.
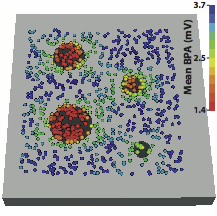
Methods and Results - We constructed a three-dimensional, in-silico, bidomain model of cardiac tissue containing transmural lesions of varying diameter. A planar excitation wave was stimulated and electrograms were sampled with a realistic catheter model at multiple positions and orientations. We carried out validation studies in animal experiments of acute ablation lesions mapped with a clinical mapping system. Bipolar electrograms sampled at higher inclination angles of the catheter with respect to the tissue demonstrated improvements in both sensitivity and specificity of lesion detection. Removing low voltage electrograms with concurrent activation of both electrodes, suggesting false attenuation of the bipolar electrogram due to alignment with the excitation wavefront, had little effect on the accuracy of voltage mapping.
Conclusions - Our results demonstrate possible mechanisms for the impact of catheter orientation on voltage mapping accuracy. Moreover, results from our simulations suggest that mapping accuracy may be improved by selectively controlling the inclination of the catheter to record at higher angles with respect to the tissue.
Keywords: arrhythmia, computer-based model, electroanatomical mapping, voltage mapping, bipolar electrogram
G.P. Bonneau, H.C. Hege, C.R. Johnson, M.M. Oliveira, K. Potter, P. Rheingans, T. Schultz.
“Overview and State-of-the-Art of Uncertainty Visualization,” In Scientific Visualization: Uncertainty, Multifield, Biomedical, and Scalable Visualization, Edited by M. Chen and H. Hagen and C.D. Hansen and C.R. Johnson and A. Kauffman, Springer-Verlag, pp. 3--27. 2014.
ISBN: 978-1-4471-6496-8
ISSN: 1612-3786
DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4471-6497-5_1
“Topological Methods in Data Analysis and Visualization III,” Edited by Peer-Timo Bremer and Ingrid Hotz and Valerio Pascucci and Ronald Peikert, Springer International Publishing, 2014.
ISBN: 978-3-319-04099-8
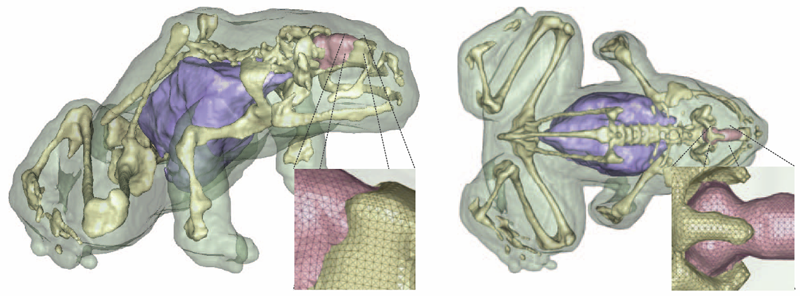
J. Bronson, J.A. Levine, R.T. Whitaker.
“Lattice cleaving: a multimaterial tetrahedral meshing algorithm with guarantees,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG), pp. 223--237. 2014.
DOI: 10.1109/TVCG.2013.115
PubMed ID: 24356365
M.S. Okun, S.S. Wu, S. Fayad, H. Ward, D. Bowers, C. Rosado, L. Bowen, C. Jacobson, C.R. Butson, K.D. Foote.
“Acute and Chronic Mood and Apathy Outcomes from a Randomized Study of Unilateral STN and GPi DBS,” In PLoS ONE, Vol. 9, No. 12, pp. e114140. December, 2014.
Objective: To study mood and behavioral effects of unilateral and staged bilateral subthalamic nucleus (STN) and globus pallidus internus (GPi) deep brain stimulation (DBS) for Parkinson's disease (PD).
Background: There are numerous reports of mood changes following DBS, however, most have focused on bilateral simultaneous STN implants with rapid and aggressive post-operative medication reduction.
Methods: A standardized evaluation was applied to a subset of patients undergoing STN and GPi DBS and who were also enrolled in the NIH COMPARE study. The Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS III), the Hamilton depression (HAM-D) and anxiety rating scales (HAM-A), the Yale-Brown obsessive-compulsive rating scale (YBOCS), the Apathy Scale (AS), and the Young mania rating scale (YMRS) were used. The scales were repeated at acute and chronic intervals. A post-operative strategy of non-aggressive medication reduction was employed.
Results: Thirty patients were randomized and underwent unilateral DBS (16 STN, 14 GPi). There were no baseline differences. The GPi group had a higher mean dopaminergic dosage at 1-year, however the between group difference in changes from baseline to 1-year was not significant. There were no differences between groups in mood and motor outcomes. When combining STN and GPi groups, the HAM-A scores worsened at 2-months, 4-months, 6-months and 1-year when compared with baseline; the HAM-D and YMRS scores worsened at 4-months, 6-months and 1-year; and the UPDRS Motor scores improved at 4-months and 1-year. Psychiatric diagnoses (DSM-IV) did not change. No between group differences were observed in the cohort of bilateral cases.
Conclusions: There were few changes in mood and behavior with STN or GPi DBS. The approach of staging STN or GPi DBS without aggressive medication reduction could be a viable option for managing PD surgical candidates. A study of bilateral DBS and of medication reduction will be required to better understand risks and benefits of a bilateral approach.
Page 38 of 144
