Visualizing Hurricanes
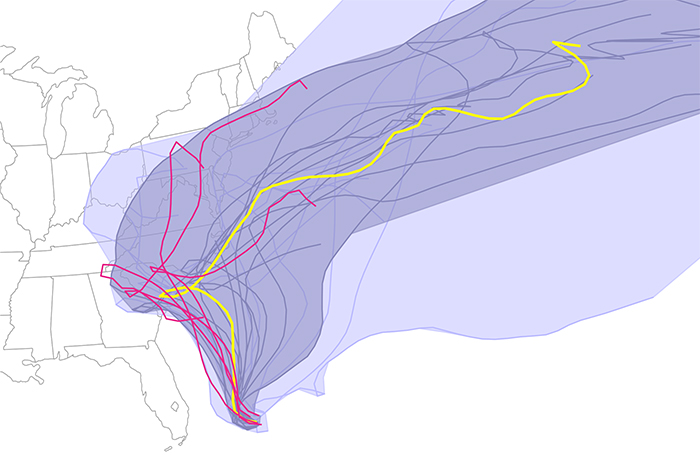 |
| The results denoted possible predicted paths, based upon different models and/or conditions Joaquin might take as of Friday October 2, 2015. Using their Curve Boxplot analysis and visualization method, they show the median hurricane path and the 50 percent band (dark region) — denoting the spatial swath in which 50 percent of the predicted hurricane tracks lie. The light band denotes nearly 100 percent of the possible paths predicted. Red denotes outliers — those hurricane paths flagged as unlikely in reference to all other members of the ensemble. |
2015 Image-Based Biomedical Modeling (IBBM) summer course
 The two-week course included the following activities:
The two-week course included the following activities:- Didactic lecture sessions given by the three PIs as well as four invited instructors and experts in their fields .
- Laboratory exercises led by a group of 10 teaching assistants and developers.
- Discussion session time for student-instructor interaction.
- A visit to the experimental and computational laboratory facilities at the University of Utah, College of Engineering to give the participants an overview of the general academic background and research projects performed at the university.
- Mentoring lectures on grant writing, responsible conduct of research, and simulation study design.
Exploring Large Data for Scientific Discovery
More elegant techniques combined with highly interdisciplinary, multi-scale collaboration are essential for dealing with massive amounts of information, plenary speaker says at the XSEDE15 conference.
A curse of dealing with mounds of data so massive that they require special tools, said computer scientist Valerio Pascucci, is if you look for something, you will probably find it, thus injecting bias into the analysis.
XSEDE15 pascucci-sg
 In his plenary talk titled "Extreme Data Management Analysis and Visualization: Exploring Large Data for Science Discovery" on July 28 during the XSEDE15 conference in St. Louis, Dr. Pascucci said that getting clean, guaranteed, unbiased results in data analyses requires highly interdisciplinary, multi-scale collaboration and techniques that unify the math and computer science behind the applications used in physics, biology, and medicine.
In his plenary talk titled "Extreme Data Management Analysis and Visualization: Exploring Large Data for Science Discovery" on July 28 during the XSEDE15 conference in St. Louis, Dr. Pascucci said that getting clean, guaranteed, unbiased results in data analyses requires highly interdisciplinary, multi-scale collaboration and techniques that unify the math and computer science behind the applications used in physics, biology, and medicine.
SCI Institute welcomes two new Professors in Computer Science and Mathematics
 Dr. Alexander Lex, School of Computing
Dr. Alexander Lex, School of Computing
Dr. Lex received his Bachelor's, Master's, and PhD degrees from the Graz University of Technology. For the past three years he was a Postdoctoral Fellow and Lecturer at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences. In 2011 he completed a research internship at the Computational Genomics Lab at the Harvard Medical School.He develops interactive data analysis methods for experts and scientists. His primary research interest is interactive data visualization and analysis, especially applied to molecular biology and pharmacology. His research is driven by the observation that there are many data analysis challenges that require human reasoning and cannot be solved automatically. He is also interested in Human Computer Interaction and Bioinformatics.
Utah team turns to computing to design clean oxy-coal boiler
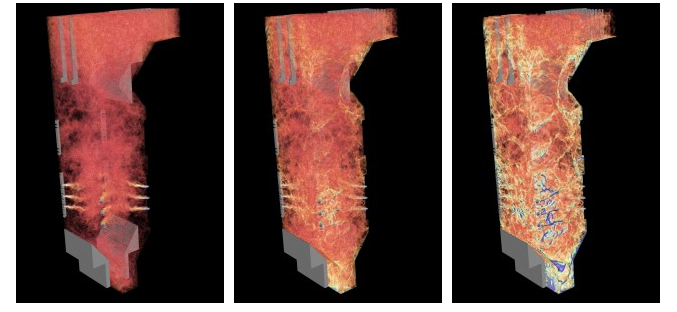 |
| A glimpse inside a coal-fired boiler. Click image to enlarge and for more information. |
Data Science: What is it and How to Teach it?
 Recently, the term big data has become ubiquitous. People who can wrangle big data are called data scientists. According to a number of sources, there is a growing need for people trained as data scientists. But what is data science? Is data science its own field or is it an interdisciplinary mix of computer science, mathematics and statistics, and domain knowledge, or perhaps is it really what statisticians have been doing all along? Since data science at scale involves large-scale computation, what is the relation between data science and computational science in research and education?
Recently, the term big data has become ubiquitous. People who can wrangle big data are called data scientists. According to a number of sources, there is a growing need for people trained as data scientists. But what is data science? Is data science its own field or is it an interdisciplinary mix of computer science, mathematics and statistics, and domain knowledge, or perhaps is it really what statisticians have been doing all along? Since data science at scale involves large-scale computation, what is the relation between data science and computational science in research and education?Read the full article on the SIAM Blogs
New Method Increases Accuracy of Ovarian Cancer Prognosis and Diagnosis
Mathematical Technique Reveals Predictive DNA Patterns That Other Methods Missed
Nearly anyone touched by ovarian cancer will tell you: it's devastating. It's bad enough that cancer in almost 80 percent of patients reaches advanced stages before diagnosis, and that most patients are expected to die within five years. But just as painfully, roughly one quarter of women diagnosed have no warning that they are resistant to platinum-based chemotherapy, the main line of defense, nor that they will likely have 18 months to live.
SIAM CSE15: Record Attendance
 The SIAM CSE15 Co-Chairs: Hans De Sterck (University of Waterloo), Chris Johnson (University of Utah), and Lois Curfman McInnes (Argonne National Laboratory) are happy to report the conclusion of a successful SIAM Computational Science and Engineering (CSE) 2015 Conference.
The SIAM CSE15 Co-Chairs: Hans De Sterck (University of Waterloo), Chris Johnson (University of Utah), and Lois Curfman McInnes (Argonne National Laboratory) are happy to report the conclusion of a successful SIAM Computational Science and Engineering (CSE) 2015 Conference.We were happy to see many of you at the 2015 SIAM Conference on CSE which took place in Salt Lake City during the past week. With 1,700 registered participants, the conference set a new attendance record for a SIAM conference.
There were 9 invited talks, 300 minisymposium sessions, 6 featured minisymposia, 100 contributed presentations, 4 panel discussions, two minitutorials, and 300 posters.
Chris Johnson to Co-Chair and Host SIAM Computational Science and Engineering Conference
 The SIAM Computational Science and Engineering 2015 Conference will be held March 14-18 at the The Calvin L. Rampton Salt Palace Convention Center, 100 S West Temple, Salt Lake City, UT 84101
The SIAM Computational Science and Engineering 2015 Conference will be held March 14-18 at the The Calvin L. Rampton Salt Palace Convention Center, 100 S West Temple, Salt Lake City, UT 84101We are expecting more than 1500 attendees. A large number of presentations will be given. See the Conference Program for details.
Both Sides of The Brain
 HOW UNIVERSITY OF UTAH HEALTH CARE REMAINS AMONG THE NATION'S BEST IN DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION (DBS)
HOW UNIVERSITY OF UTAH HEALTH CARE REMAINS AMONG THE NATION'S BEST IN DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION (DBS)From University of Utah Clinical Neurosciences Center Convergence (See page 12)
By Jennifer Dobner
It sounds like something straight from a scene in a science fiction film: Surgery that places a set of wires under the skull so that electrical signals can be transmitted to different areas of the brain. It's called DBS, or deep brain stimulation. And if the idea of it seems a bit wince-inducing or scary, then understanding the power of what it can do - quiet the tremors associated with Parkinson's disease and other brain disorders - will likely wash away any patient's fears.
