SCI Publications
2013
Bei Wang, P. Rosen, P. Skraba, H. Bhatia, V. Pascucci.
“Visualizing Robustness of Critical Points for 2D Time-Varying Vector Fields,” In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 32, No. 3, Wiley-Blackwell, pp. 221--230. jun, 2013.
DOI: 10.1111/cgf.12109
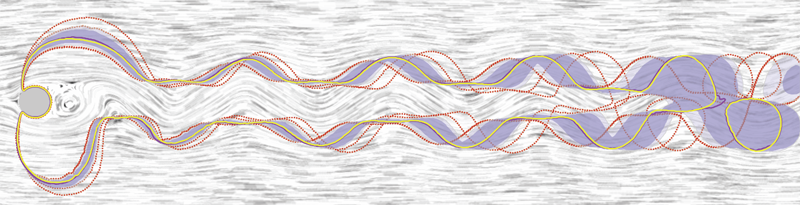
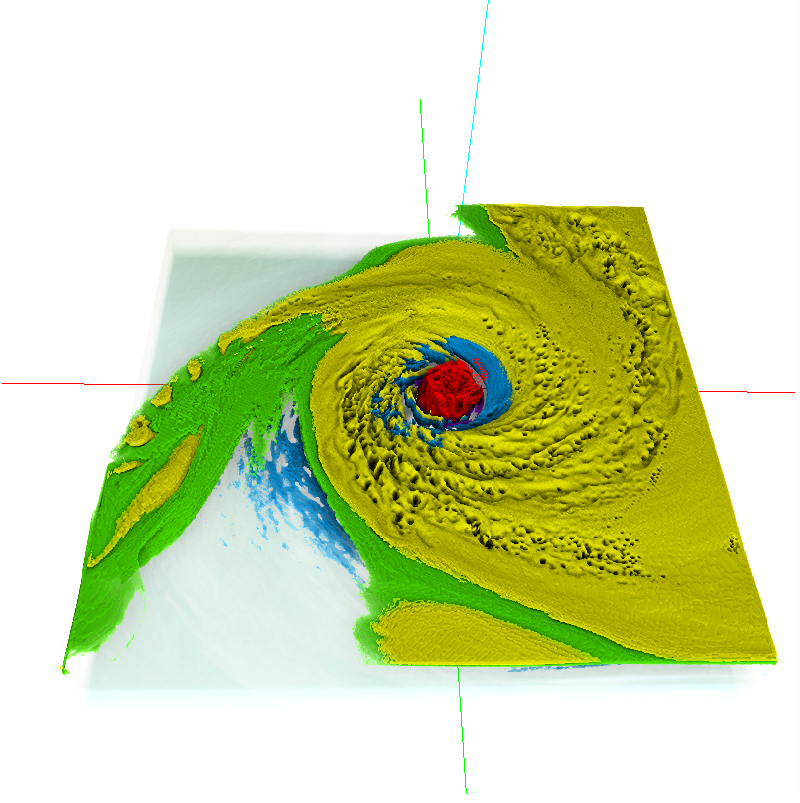
Analyzing critical points and their temporal evolutions plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of vector fields. A key challenge is to quantify the stability of critical points: more stable points may represent more important phenomena or vice versa. The topological notion of robustness is a tool which allows us to quantify rigorously the stability of each critical point. Intuitively, the robustness of a critical point is the minimum amount of perturbation necessary to cancel it within a local neighborhood, measured under an appropriate metric. In this paper, we introduce a new analysis and visualization framework which enables interactive exploration of robustness of critical points for both stationary and time-varying 2D vector fields. This framework allows the end-users, for the first time, to investigate how the stability of a critical point evolves over time. We show that this depends heavily on the global properties of the vector field and that structural changes can correspond to interesting behavior. We demonstrate the practicality of our theories and techniques on several datasets involving combustion and oceanic eddy simulations and obtain some key insights regarding their stable and unstable features.
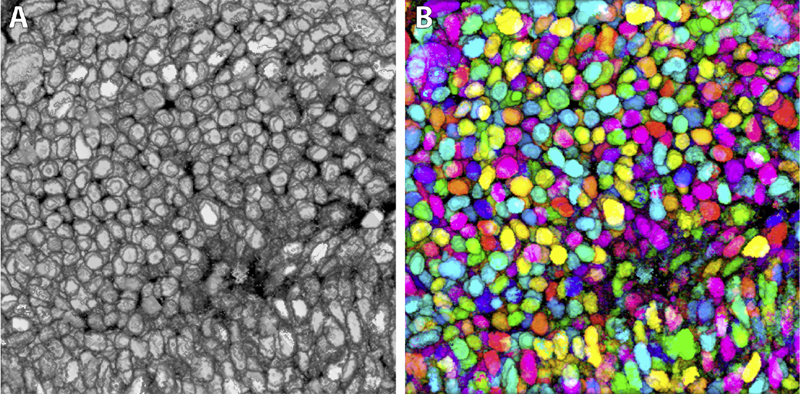
Y. Wan, H. Otsuna, C.D. Hansen.
“Synthetic Brainbows,” In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 32, No. 3pt4, Wiley-Blackwell, pp. 471--480. jun, 2013.
DOI: 10.1111/cgf.12134
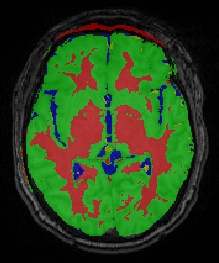
Bo Wang, M. Prastawa, A. Saha, S.P. Awate, A. Irimia, M.C. Chambers, P.M. Vespa, J.D. Van Horn, V. Pascucci, G. Gerig.
“Modeling 4D changes in pathological anatomy using domain adaptation: analysis of TBI imaging using a tumor database,” In Proceedings of the 2013 MICCAI-MBIA Workshop, Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS), Vol. 8159, Note: Awarded Best Paper!, pp. 31--39. 2013.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-02126-3_4
Y. Wan.
“Fluorender, An Interactive Tool for Confocal Microscopy Data Visualization and Analysis,” Note: Ph.D. Thesis, School of Computing, University of Utah, June, 2013.
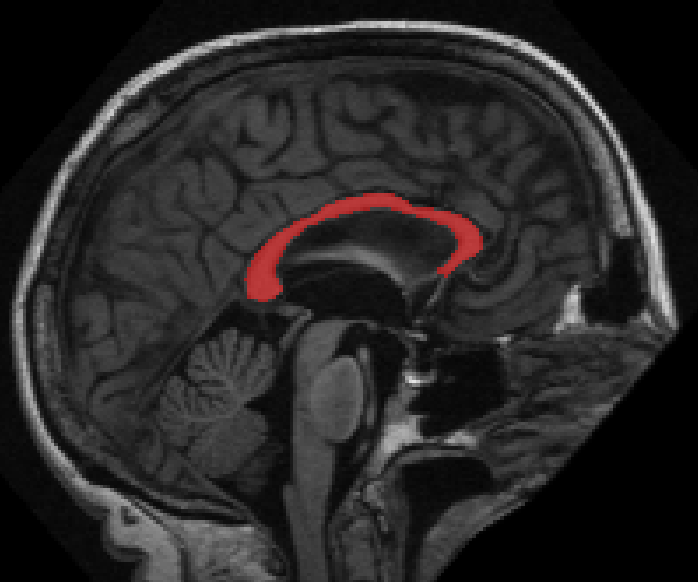
Confocal microscopy has become a popular imaging technique in biology research in recent years. It is often used to study three-dimensional (3D) structures of biological samples. Confocal data are commonly multi-channel, with each channel resulting from a different fluorescent staining. This technique also results finely detailed structures in 3D, such as neuron fibers. Despite the plethora of volume rendering techniques that have been available for many years, there is a demand from biologists for a flexible tool that allows interactive visualization and analysis of multi-channel confocal data. Together with biologists, we have designed and developed FluoRender. It incorporates volume rendering techniques such as a two-dimensional (2D) transfer function and multi-channel intermixing. Rendering results can be enhanced through tone-mappings and overlays. To facilitate analyses of confocal data, FluoRender provides interactive operations for extracting complex structures. Furthermore, we developed the Synthetic Brainbow technique, which takes advantage of the asynchronous behavior in Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) framebuffer loops and generates random colorizations for different structures in single-channel confocal data. The results from our Synthetic Brainbows, when applied to a sequence of developing cells, can then be used for tracking the movements of these cells. Finally, we present an application of FluoRender in the workflow of constructing anatomical atlases.
Keywords: confocal microscopy, visualization, software
G.H. Weber, K. Beketayev, P.-T. Bremer, B. Hamann, M. Haranczyk, M. Hlawitschka, V. Pascucci.
“Comprehensible Presentation of Topological Information,” No. LBNL-5693E, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 2013.
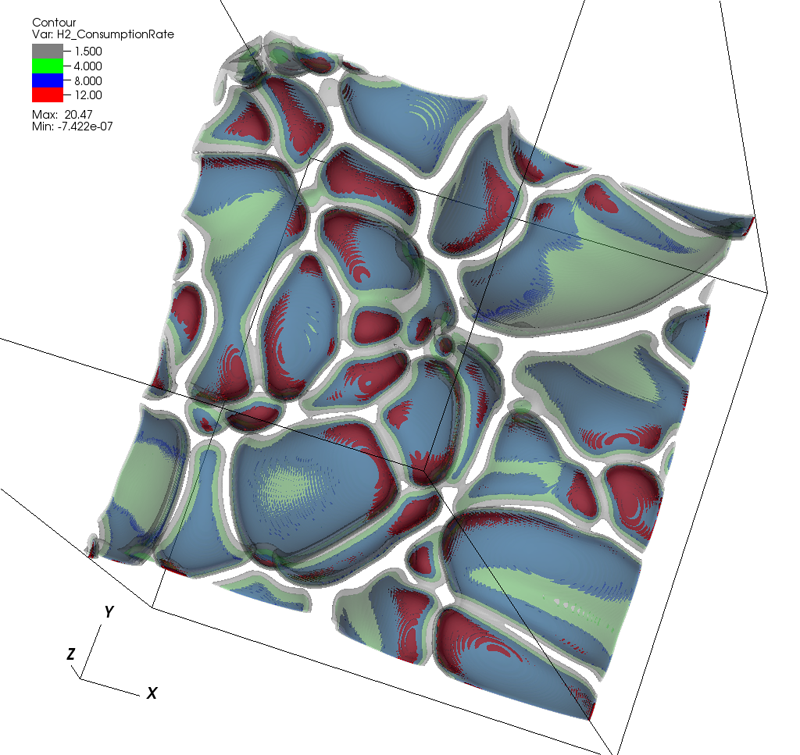
R.T. Whitaker, M. Mirzargar, R.M. Kirby.
“Contour Boxplots: A Method for Characterizing Uncertainty in Feature Sets from Simulation Ensembles,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 19, No. 12, pp. 2713--2722. December, 2013.
DOI: 10.1109/TVCG.2013.143
PubMed ID: 24051838
W. Widanagamaachchi, P. Rosen, V. Pascucci.
“A Flexible Framework for Fusing Image Collections into Panoramas,” In Proceedings of the 2013 SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns, and Images, Note: Awarded Best Paper., pp. 195-202. 2013.
DOI: 10.1109/SIBGRAPI.2013.35

E. Wong, S.P. Awate, P.T. Fletcher.
“Adaptive Sparsity in Gaussian Graphical Models,” In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), pp. (accepted). 2013.
An effective approach to structure learning and parameter estimation for Gaussian graphical models is to impose a sparsity prior, such as a Laplace prior, on the entries of the precision matrix. Such an approach involves a hyperparameter that must be tuned to control the amount of sparsity. In this paper, we introduce a parameter-free method for estimating a precision matrix with sparsity that adapts to the data automatically. We achieve this by formulating a hierarchical Bayesian model of the precision matrix with a noninformative Jeffreys' hyperprior. We also naturally enforce the symmetry and positivede definiteness constraints on the precision matrix by parameterizing it with the Cholesky decomposition. Experiments on simulated and real (cell signaling) data demonstrate that the proposed approach not only automatically adapts the sparsity of the model, but it also results in improved estimates of the precision matrix compared to the Laplace prior model with sparsity parameter chosen by cross-validation.
M. Zhang, N.P. Singh, P.T. Fletcher.
“Bayesian Estimation of Regularization and Atlas Building in Diffeomorphic Image Registration,” In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI), Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS), pp. (accepted). 2013.

M. Zhang, P.T. Fletcher.
“Probabilistic Principal Geodesic Analysis,” In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), pp. (accepted). 2013.
L. Zhou, C.D. Hansen.
“Transfer Function Design based on User Selected Samples for Intuitive Multivariate Volume Exploration,” In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Pacific Visualization Symposium (PacificVis), pp. 73--80. 2013.
ISSN: 2165-8765
DOI: 10.1109/PacificVis.2013.6596130
L. Zhou, C.D. Hansen.
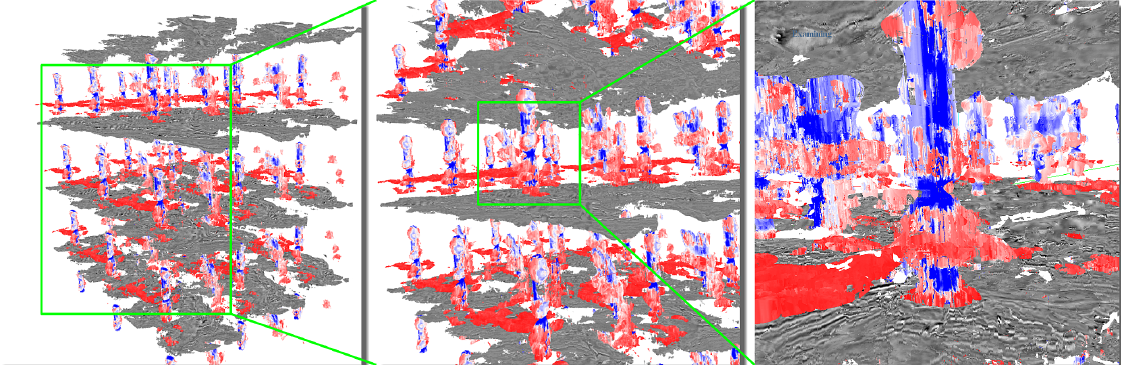
“Interactive rendering and efficient querying for large multivariate seismic volumes on consumer level PCs,” In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Symposium on Large-Scale Data Analysis and Visualization (LDAV), pp. 117--118. 2013.
DOI: 10.1109/LDAV.2013.6675167
X. Zhu, Y. Gur, W. Wang, P.T. Fletcher.
“Model Selection and Estimation of Multi-Compartment Models in Diffusion MRI with a Rician Noise Model,” In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI), Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS), Vol. 23, pp. 644--655. 2013.
PubMed ID: 24684006

2012
Y.-J. Ahn, C. Hoffmann, P. Rosen.
“A Note on Circle Packing,” In Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE C, Vol. 13, No. 8, pp. 559--564. 2012.
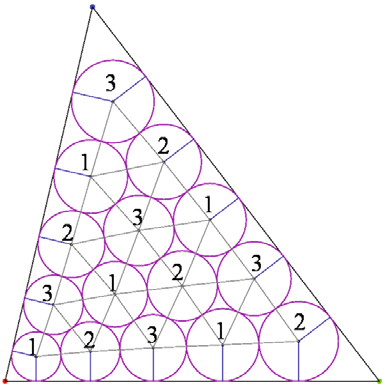
Keywords: Circle packing, Algorithm performance, Parallel computation, Graphics processing unit (GPU)
N.W. Akoum, C.J. McGann, G. Vergara, T. Badger, R. Ranjan, C. Mahnkopf, E.G. Kholmovski, R.S. Macleod, N.F. Marrouche.
“Atrial Fibrosis Quantified Using Late Gadolinium Enhancement MRI is AssociatedWith Sinus Node Dysfunction Requiring Pacemaker Implant,” In Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, Vol. 23, No. 1, pp. 44--50. 2012.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2011.02140.x
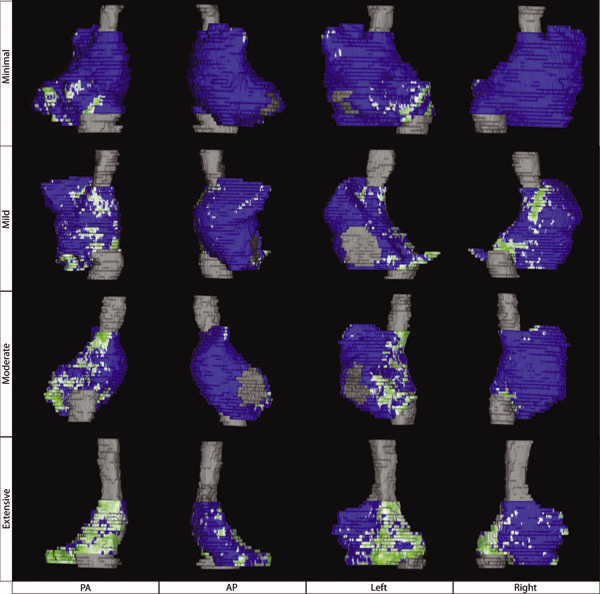
Atrial Fibrosis and Sinus Node Dysfunction. Introduction: Sinus node dysfunction (SND) commonly manifests with atrial arrhythmias alternating with sinus pauses and sinus bradycardia. The underlying process is thought to be because of atrial fibrosis. We assessed the value of atrial fibrosis, quantified using Late Gadolinium Enhanced-MRI (LGE-MRI), in predicting significant SND requiring pacemaker implant.
Methods: Three hundred forty-four patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) presenting for catheter ablation underwent LGE-MRI. Left atrial (LA) fibrosis was quantified in all patients and right atrial (RA) fibrosis in 134 patients. All patients underwent catheter ablation with pulmonary vein isolation with posterior wall and septal debulking. Patients were followed prospectively for 329 ± 245 days. Ambulatory monitoring was instituted every 3 months. Symptomatic pauses and bradycardia were treated with pacemaker implantation per published guidelines.
Results: The average patient age was 65 ± 12 years. The average wall fibrosis was 16.7 ± 11.1% in the LA, and 5.3 ± 6.4% in the RA. RA fibrosis was correlated with LA fibrosis (R2= 0.26; P < 0.01). Patients were divided into 4 stages of LA fibrosis (Utah I: 35%). Twenty-two patients (mean atrial fibrosis, 23.9%) required pacemaker implantation during follow-up. Univariate and multivariate analysis identified LA fibrosis stage (OR, 2.2) as a significant predictor for pacemaker implantation with an area under the curve of 0.704.
Conclusions: In patients with AF presenting for catheter ablation, LGE-MRI quantification of atrial fibrosis demonstrates preferential LA involvement. Significant atrial fibrosis is associated with clinically significant SND requiring pacemaker implantation. (J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, Vol. 23, pp. 44-50, January 2012)
G.A. Ateshian, S.A. Maas, J.A. Weiss.
“Solute transport across a contact interface in deformable porous media,” In Journal of Biomechanics, Vol. 45, No. 6, pp. 1023-–1027. 2012.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2012.01.003
A finite element formulation of neutral solute transport across a contact interface between deformable porous media is implemented and validated against analytical solutions. By reducing the integral statements of external virtual work on the two contacting surfaces into a single contact integral, the algorithm automatically enforces continuity of solute molar flux across the contact interface, whereas continuity of the effective solute concentration (a measure of the solute mechano-chemical potential) is achieved using a penalty method. This novel formulation facilitates the analysis of problems in biomechanics where the transport of metabolites across contact interfaces of deformable tissues may be of interest. This contact algorithm is the first to address solute transport across deformable interfaces, and is made available in the public domain, open-source finite element code FEBio (http://www.febio.org).
Keywords: FEBio, Finite element modeling, Contact mechanics, Solute transport, Porous media, Biphasic theory
S.P. Awate, P. Zhu, R.T. Whitaker.
“How Many Templates Does It Take for a Good Segmentation?: Error Analysis in Multiatlas Segmentation as a Function of Database Size,” In Int. Workshop Multimodal Brain Image Analysis (MBIA) at Int. Conf. MICCAI, Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS), Vol. 2, Note: Recieved Best Paper Award, pp. 103--114. 2012.
PubMed ID: 24501720
PubMed Central ID: PMC3910563
A. Barg, N. Knupp, H.B. Henninger, L. Zwicky, B. Hintermann.
“Total ankle replacement using HINTEGRA, an unconstrained, three-component system: surgical technique and pitfalls,” In Foot and Ankle Clinics, Vol. 17, No. 4, pp. 607--635. 2012.
DOI: 10.1016/j.fcl.2012.08.006
A. Barg, G.I. Pagenstert, A.G. Leumann, A.M. Müller, H.B. Henninger, V. Valderrabano.
“Treatment of the Arthritic Valgus Ankle,” In Foot and Ankle Clinics, Vol. 17, No. 4, pp. 647--663. 2012.
DOI: 10.1016/j.fcl.2012.08.007
A. Barg, M.D. Harris, H.B. Henninger, R.L. Amendola, C.L. Saltzman, B. Hintermann, A.E. Anderson.
“Medial distal tibial angle: comparison between weightbearing mortise view and hindfoot alignment view,” In Foot & Ankle International, Vol. 33, No. 8, pp. 655--661. 2012.
DOI: 10.3113/FAI.2012.0655
Background: The medial distal tibial angle (MDTA) is used to determine ankle alignment. The mortise view is the standard to measure MDTA, but the hindfoot alignment view (HAV) has become popular. The MDTA may vary between views, influencing the choice of surgery.
Methods: The MDTA was compared between the mortise and HAV in 146 ankles. MDTA was correlated to age and sagittal tibial tilt for each view. Differences in MDTA by gender and ethnicity were assessed. Diagnostic agreement (varus, valgus, normal) between views was calculated. Clinical assessment of alignment was determined and percent agreement between clinical and radiographic alignment was quantified.
Results: The MDTA measured from the mortise view and HAV radiographs was 89.0 (range, 81 to 96 degrees; SD = 2.8) degrees and 86.0 (range, 73 to 95 degrees; SD = 3.5) degrees, respectively. The MDTA was comparable for both genders for mortise (p = 0.356) and HAV (p = 0.621). The MDTA was comparable in all ethnic groups for mortise view (p = 0.616) and HAV (p = 0.916). Correlation between the measured MDTA and age was not statistically significant for both the mortise (r = 0.118; p = 0.158) and HAV (r = 0.148; p = 0.074). In only 47.3% of all ankles was the radiographic diagnosis of alignment the same between views. Agreement between clinical and radiographic classifications was 60.3% for the mortise view and 52.8% for the HAV.
Conclusion: Substantial disagreement in primary alignment was found between the mortise and HAV as quantified by the MDTA. Agreement between clinical and radiographic alignment was also poor. Clinical Relevance: Advanced imaging such as CT or MRI may better describe ankle alignment.
Page 50 of 144
