SCI Publications
2009


K. Potter, A. Wilson, P.-T. Bremer, D. Williams, C. Doutriaux, V. Pascucci, C.R. Johhson.
“Visualization of Uncertainty and Ensemble Data: Exploration of Climate Modeling and Weather Forecast Data with Integrated ViSUS-CDAT Systems,” In J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., Vol. 180, No. 012089, IOP Publishing, pp. 012089. July, 2009.
DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/180/1/012089


K. Potter, A. Wilson, P.-T. Bremer, D. Williams, C. Doutriaux, V. Pascucci, C.R. Johnson.
“Ensemble-Vis: A Framework for the Statistical Visualization of Ensemble Data,” In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, pp. 233--240. 2009.


M.W. Prastawa, E. Bullitt, G. Gerig.
“Simulation of brain tumors in MR images for evaluation of segmentation efficacy,” In Med Image Anal, Vol. 13, No. 2, pp. 297--311. 2009.
PubMed ID: 19119055


J.S. Preston, T. Tasdizen, C.M. Terry, A.K. Cheung, R.M. Kirby.
“Using the stochastic collocation method for the uncertainty quantification of drug concentration due to depot shape variability,” In IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, Vol. 56, No. 3, Note: Epub 2008 Dec 2, pp. 609--620. 2009.
PubMed ID: 19272865


E.J. Rainis, S.A. Maas, H.B. Henninger, P.J. McMahon, J.A. Weiss, R.E. Debski.
“Material properties of the axillary pouch of the glenohumeral capsule: Is isotropic material symmetry appropriate?,” In Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, Vol. 131, No. 13, pp. (7 pages). 2009.


E. Santos, D. Koop, H.T. Vo, E. Anderson, J. Freire, C.T. Silva.
“Using Workflow Medleys to Streamline Exploratory Tasks,” In 21st International Conference on Scientific and Statistical Database Management (SSDBM), pp. 292--301. 2009.


E. Santos, L. Lins, J.P. Ahrens, J. Freire, C.T. Silva.
“VisMashup: Streamlining the Creation of Custom Visualization Applications,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Visualization Conference, Vol. 15, No. 6, pp. 1539--1546. Sept/Oct, 2009.
DOI: 10.1109/TVCG.2009.195


A.R. Sanderson, M.D. Meyer, R.M. Kirby, C.R. Johnson.
“A Framework for Exploring Numerical Solutions of Advection Reaction Diffusion Equations using a GPU Based Approach,” In Journal of Computing and Visualization in Science, Vol. 12, pp. 155--170. 2009.
DOI: 10.1007/s00791-008-0086-0


D. Sato, Y. Xie, J.N. Weiss, Z. Qu, A. Garfinkel, A.R. Sanderson.
“Acceleration of Cardiac Tissue Simulation with Graphic Processing Units,” In Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing, Note: Published online Aug 5, 2009, 2009.
DOI: 10.1007/s11517-0


M. Schott, V. Pegoraro, C.D. Hansen, K. Boulanger, K. Bouatouch.
“A Directional Occlusion Shading Model for Interactive Direct Volume Rendering,” In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 28, No. 3, Wiley-Blackwell, pp. 855--862. jun, 2009.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-8659.2009.01464.x


J.M. Schreiner.
“Uniform and Adaptive (Re)meshing of Surfaces,” Note: Ph.D. Thesis, School of Computing, University of Utah, June, 2009.


N.M. Segerson, M. Daccarett, T.J. Badger, A. Shabaan, N. Akoum, E.N. Fish, S. Rao, N.S. Burgon, Y. Adjei-Poku, E.G. Kholmovski, S. Vijayakumar, E.V.R. Dibella, R.S. Macleod, N.F. Marrouche.
“Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Confirmed Ablative Debulking of the Left Atrial Posterior Wall and Septum for Treatment of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: Rationale and Initial Experience,” In Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, Vol. 21, No. 2, pp. 126--132. 2009.


J.F. Shepherd, C.R. Johnson.
“Hexahedral Mesh Generation for Biomedical Models in SCIRun,” In Engineering with Computers, Vol. 25, No. 1, pp. 97--114. 2009.


F. Shi, P.T. Yap, Y. Fan, J.Z. Cheng, L.L. Wald, G. Gerig, W. Lin, D. Shen.
“Cortical Enhanced Tissue Segmentation of Neonatal Brain MR Images Acquired by a Dedicated Phased Array Coil,” In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 39--45. 2009.
PubMed ID: 20862268


M. Steffen.
“Analysis-Guided Improvements of the Material Point Method,” School of Computing, University of Utah, 2009.
The Material Point Method (MPM) has shown itself to be a powerful tool in the simulation of large deformation problems, especially those involving complex geometries and contact where typical finite element type methods frequently fail. While these large complex problems lead to some impressive simulations and solutions, there has been a lack of basic analysis characterizing the errors present in the method, even on the simplest of problems. However, like most methods which employ mixed Lagrangian (particle) and Eulerian strategies, analysis of the method is not straight forward. The lack of an analysis framework for MPM, as is found in finite element methods, makes it challenging to explain anomalies found in its employment and makes it difficult to propose methodology improvements with predictable outcomes. In this dissertation, we provide a formal analysis of the errors in MPM and use this analysis to direct proposed improvements. In particular, we will focus on how the lack of regularity in the grid functions used for representing the solution can hamper both spatial and temporal convergence of the method. We will show how the use of smoother basis functions, such as B-splines, can improve the accuracy of the method. An in-depth analysis of the current time stepping methods will help to explain behavior currently demonstrated numerically in the literature and will allow users of the method to understand the balance of spatial and temporal errors in MPM. Lastly, extrapolation techniques will be proposed to improve quadrature errors in the method.


M. Streit, A. Lex, H. Müller, D. Schmalstieg.
“Gaze-Based Focus Adaption in an Information Visualization System,” In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Graphics and Visualization and Image Processing (CGVCVIP '09), 2009.
As the complexity and amount of real world data continuously grows, modern visualization systems are changing. Traditional information visualization techniques are often not sufficient to allow an in-depth visual data exploration process. Multiple view systems combined with linking & brushing are only one building block of a successful InfoVis system. In this paper we propose the incorporation of cheap and simple gaze-based interaction. We employ the tracking information not for selecting data (i.e. mouse interaction) but for an intelligent adaption of 2D and 3D visualizations. Derived from the focus+context paradigm, we call this gaze-focus. The proposed methods are demonstrated by means of three different visualizations.


M. Streit, A. Lex, M. Kalkusch, K. Zatloukal, D. Schmalstieg.
“Caleydo: Connecting Pathways with Gene Expression,” In Bioinformatics, Vol. 25, No. 20, pp. 2760--2761. 2009.
Understanding the relationships between pathways and the altered expression of their components in disease conditions can be addressed in a visual data analysis process. Caleydo uses novel visualization techniques to support life science experts in their analysis of gene expression data in the context of pathways and functions of individual genes. Pathways and gene expression visualizations are placed in a 3D scene where selected entities (i.e. genes) are visually connected. This allows Caleydo to seamlessly integrate interactive gene expression visualization with cross-database pathway exploration.


R. Tao, P.T. Fletcher, R.T. Whitaker.
“A Variational Image-Based Approach to the Correction of Susceptibility Artifacts in the Alignment of Diffusion Weighted and Structural MRI,” In Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer, pp. 664--675. 2009.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-02498-6_55
PubMed ID: 19694302


T. Tasdizen.
“Principal neighborhood dictionaries for nonlocal means image denoising,” In IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, Vol. 18, No. 12, Note: Epub 2009 Jul 24, pp. 2649--2660. 2009.
PubMed ID: 19635697


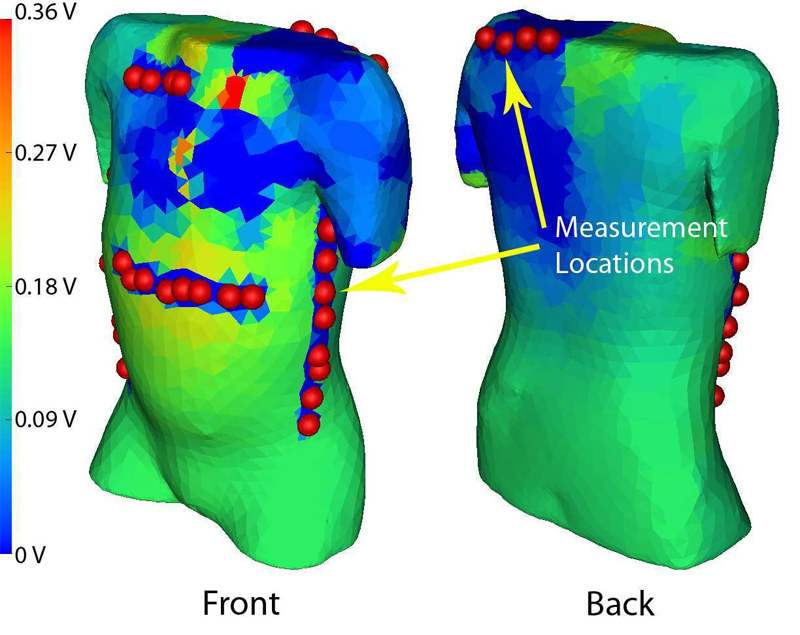
J.D. Tate, J.G. Stinstra, T. Pilcher, and R.S. MacLeod.
“Measuring Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs) During Implantation Surgery: Verification of a Simulation,” In Computers in Cardiology, pp. 473--476. 2009.
ISSN: 0276-6547
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) are increasing used in abnormal configurations. We have developed a patient specific forward simulation model to predict efficacy of the defibrillation shock. Our goal was to develop a method of measuring the ICD surface potentials as the devices are tested during implantation surgery to use as verification of the simulation. A lead selection algorithm was used to develop a surface potential mapping system with 32 recording sites that do not interfere with implantation surgery. ICD discharge recordings were compared at similar locations to corresponding patient models. The reconstructed simulated surface potentials showed