SCI Publications
2008


J. Krüger.
“A GPU Framework for Interactive Simulation and Rendering of Fluid Effects,” In IT - Information Technology, Vol. 4, pp. 265--268. 2008.


J. Krüger, K. Potter, R.S. MacLeod, C.R. Johnson.
“Unified Volume Format: A General System For Efficient Handling Of Large Volumetric Datasets,” In Proceedings of IADIS Computer Graphics and Visualization 2008 (CGV 2008), pp. 19--26. 2008.
PubMed ID: 20953270
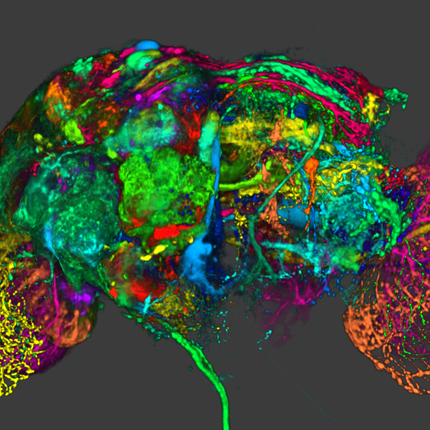
With the continual increase in computing power, volumetric datasets with sizes ranging from only a few megabytes to petascale are generated thousands of times per day. Such data may come from an ordinary source such as simple everyday medical imaging procedures, while larger datasets may be generated from cluster-based scientific simulations or measurements of large scale experiments. In computer science an incredible amount of work worldwide is put into the efficient visualization of these datasets. As researchers in the field of scientific visualization, we often have to face the task of handling very large data from various sources. This data usually comes in many different data formats. In medical imaging, the DICOM standard is well established, however, most research labs use their own data formats to store and process data. To simplify the task of reading the many different formats used with all of the different visualization programs, we present a system for the efficient handling of many types of large scientific datasets (see Figure 1 for just a few examples). While primarily targeted at structured volumetric data, UVF can store just about any type of structured and unstructured data. The system is composed of a file format specification with a reference implementation of a reader. It is not only a common, easy to implement format but also allows for efficient rendering of most datasets without the need to convert the data in memory.

M. Kubicki, M. Styner, S. Bouix, G. Gerig, D. Markant, K. Smith, R. Kikinis, R.W. McCarley, M.E. Shenton.
“Reduced Interhemispheric Connectivity in Schizophrenia- Tractography Based Segmentation of the Corpus Callosum,” In Schizophrenia Research, Vol. 106, No. 2-3, pp. 125--131. December, 2008.


C. Ledergerber, G. Guennebaud, M.D. Meyer, M. Bacher, H. Pfister.
“Volume MLS Ray Casting,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (Proceedings of Visualization 2008), Vol. 14, No. 6, pp. 1539--1546. 2008.
The method of Moving Least Squares (MLS) is a popular framework for reconstructing continuous functions from scattered data due to its rich mathematical properties and well-understood theoretical foundations. This paper applies MLS to volume rendering, providing a unified mathematical framework for ray casting of scalar data stored over regular as well as irregular grids. We use the MLS reconstruction to render smooth isosurfaces and to compute accurate derivatives for high-quality shading effects. We also present a novel, adaptive preintegration scheme to improve the efficiency of the ray casting algorithm by reducing the overall number of function evaluations, and an efficient implementation of our framework exploiting modern graphics hardware. The resulting system enables high-quality volume integration and shaded isosurface rendering for regular and irregular volume data.


S. Lew, C.H. Wolters, A. Anwander, S. Makeig, R.S. Macleod.
“Improved EEG Source Analysis Using Low-Resolution Conductivity Estimation in a Four-Compartment Finite Element Head Model,” In Human Brain Mapping, Vol. 31, December, 2008.


G.-S. Li, X. Tricoche, D. Weiskopf, C.D. Hansen.
“Flow Charts: Visualization of Vector Fields on Arbitrary Surfaces,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, Vol. 14, No. 5, pp. 1--14. September/October, 2008.


G.-S. Li, X. Tricoche, C.D. Hansen.
“Physically-based Dye Advection for Flow Visualization,” In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 27, No. 3, Edited by A. Vilanova and A. Telea and G. Scheuermann and T. Moeller, Wiley-Blackwell, pp. 727--734. May, 2008.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-8659.2008.01201.x


J. Li, D. Xiu.
“On Numerical Properties of the Ensemble Kalman Filter for Data Assimilation,” In Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, Vol. 197, No. 43--44, pp. 3574--3583. 2008.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cma.2008.03.022
Ensemble Kalman filter (EnKF) has been widely used as a sequential data assimilation method, primarily due to its ease of implementation resulting from replacing the covariance evolution in the traditional Kalman filter (KF) by an approximate Monte Carlo ensemble sampling. In this paper rigorous analysis on the numerical errors of the EnKF is conducted in a general setting. Error bounds are provided and convergence of the EnKF to the exact Kalman filter is established. The analysis reveals that the ensemble errors induced by the Monte Carlo sampling can be dominant, compared to other errors such as the numerical integration error of the underlying model equations. Methods to reduce sampling errors are discussed. In particular, we present a deterministic sampling strategy based on cubature rules (qEnKF) which offers much improved accuracy. The analysis also suggests a less obvious fact — more frequent data assimilation may lead to larger numerical errors of the EnKF. Numerical examples are provided to verify the theoretical findings and to demonstrate the improved performance of the qEnKF.
Keywords: Data assimilation, Uncertainty quantification, Ensemble Kalman filter


L. Lins, D. Koop, E.W. Anderson, S.P. Callahan, E. Santos, C.E. Scheidegger, J. Freire, C.T. Silva.
“Examining Statistics of Workflow Evolution Provenance: A First Study,” In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Scientific and Statistical Database Management (SSDBM), pp. 573--579. 2008.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-69497-7_40


W. Lin, Q. Zhu, W. Gao, Y. Chen, C.-H. Toh, M. Styner, G. Gerig, J.K. Smith, B. Biswal, J. Gilmore.
“Functional Connectivity Magnetic Resonance Imaging Reveals Cortical Functional Connectivity in the Developing Brain,” In American Journal of Neuroradiology, Vol. 29, pp. 1883--1889. Fall, 2008.


Y. Livnat, S.G. Parker, C.R. Johnson.
“Fast Isosurface Extraction Methods for Large Image Data Sets,” In Handbook of Medical Image Processing and Analysis, 2nd edition, Ch. 47, Note: (to appear), Edited by Isaac N. Bankman, Elsevier, pp. 801--816. 2008.


M. Lizier, J.F. Shepherd, L.G. Nonato, J. Comba, C.T. Silva.
“Comparing Techniques for Tetrahedral Mesh Generation,” In Proceedings of the Inaugural International Conference of the Engineering Mechanics Institute (EM 2008), pp. (accepted). 2008.


J. Luitjens, Q. Meng, M. Berzins, T. Henderson.
“Improving the Load Balance of Parallel Adaptive Mesh Refined Simulations,” SCI Technical Report, No. UUSCI-2008-007, University of Utah School of Computing, 2008.


J. Luitjens, B. Worthen, M. Berzins, T. Henderson.
“Scalable Parallel AMR for the Uintah Multiphysics Code,” In Petascale Computing Algorithms and Applications, Ch. 4, CRC Press LLC., pp. 67--82. 2008.


T.J. Lujan, C.J. Underwood, N.T. Jacobs, J.A. Weiss.
“Contribution of Glycosaminoglycans to Viscoelastic Tensile Behavior of Human Ligament,” In Journal of Applied Physiology, Vol. 106, No. 2, pp. 423--431. 2008.


T. Martin, E. Cohen, R.M. Kirby.
“Volumetric Parameterization and Trivariate B-spline Fitting using Harmonic Functions,” In Proceedings of ACM Solid and Physical Modeling, Stony Brook, NY, Note: Awarded Best Paper, pp. 269-280. 2008.


C.J. McGann, E.G. Kholmovski, R.S. Oakes, J.J. Blauer, M. Daccarett, N. Segerson, K.J. Airey, N. Akoum, E. Fish, T.J. Badger, E.V. DiBella, D.L. Parker, R.S. MacLeod, N.F. Marrouche.
“New Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Method for Defining the Extent of Left Atrial Wall Injury After the Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation,” In Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Vol. 52, No. 15, pp. 1263--1271. Oct 7, 2008.


Q. Meng, J. Luitjens, M. Berzins.
“A Comparison of Load Balancing Algorithms for AMR in Uintah,” SCI Technical Report, No. UUSCI-2008-006, University of Utah, 2008.


S. Mergen, C. Heuser, J. Freire.
“Querying Structured Information Sources on the Web,” In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Information Integration and Web-based Applications and Services, pp. 470--476. 2008.


D. Merck, G. Tracton, R. Saboo, J. Levy, E. Chaney, S. Pizer, S. Joshi.
“Training models of anatomic shape variability,” In Medical Physics, Vol. 35, No. 8, pp. 3584--3596. 2008.
PubMed ID: 18777919